Firewall
New firewall features include:
- Menu Simplification
- Unified Policy Management
- Importing LDAP Users for a Security Policy
- Dynamic VIP According to DNS Translation
- GTP Rate Limiting
- Object UUID Support
- Configuring the Class of Service Bit
- Hairpinning for NAT64 and NAT46
- Maximum Number of Available Virtual IPs Increased
Menu Simplification
Security policies and firewall objects are now found in the same menu, called Policy & Objects.
Policies
The menu option for policies, found at Policy & Objects > Policy, has been expanded to include the following policy types:
- IPv4
- IPv6
- NAT64
- NAT46
- DoS
- IPv6 DoS
- Multicast
- Local In
- Central NAT Table
- Proxy Options
- SSL Inspection (SSL/SSH Inspection on some FortiGate models)
Objects
The following firewall objects have been grouped together under a single menu, found at Policy & Objects > Objects:
- Addresses
- Services
- Schedules
- Traffic Shapers
- Virtual IPs
- IP Pools
Other changes have been made for specific features.
Groups
Object groups can now be made by expanding the arrow beside Create New and selecting Group.
Traffic Shapers
Shared and Per-IP shapers have been combined into a single page, with a Type field added to the creation page.
Traffic shapers creation screen
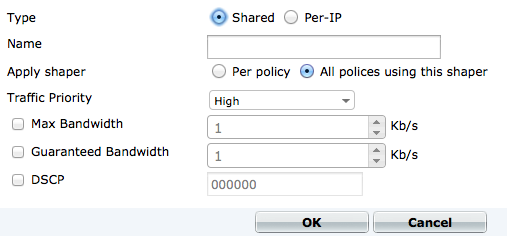
An additional column, Type, has also been added to the traffic shapers table.
Unified Policy Management
The different creation pages in the web-based manager for policy types and subtypes (user-identity, device identity, and VPN) have been merged into a single main policy creation page. New fields have been added for Source User(s) and Source Device Type that remove the need for multiple authentication rules in a single policy. This allows for greater control and customization of policies, as a combination of these source types can be used in a single policy rather than having to pick one type.
The policy creation page
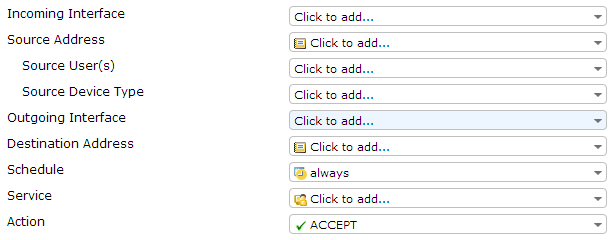
If both Source User(s) and Source Device Type are set, then traffic must match both fields in order to be accepted by the policy. Both these fields are optional; only Source Address must be set.
For policies that require user or device authentication, there is an implicit fall-through to allow traffic to be checked against other policies if it does not match the authentication requirements. This option cannot be disabled and the CLI command set fall-through-unauthenticated has been removed.
For more information about security policies in FortiOS 5.2, please see the FortiGate Cookbook recipe Creating security policies.
To create a policy for SSL VPNs, an SSL VPN interface is created and used as the source interface. For more information about this interface creation, see SSL VPN Configuration.
Importing LDAP Users for a Security Policy
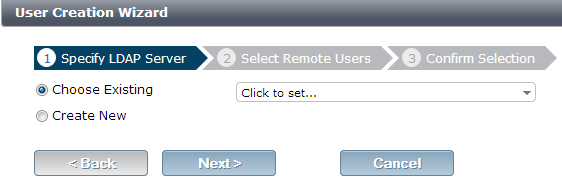
The LDAP user importing wizard can now be launched during the creation of a new security policy, by selecting Import LDAP users in the dropdown menu when you are adding users to the policy.
The LDAP user importing wizard
Dynamic VIP According to DNS Translation
Dynamic virtual IPs according to DNS translation can now be configured.
When a dynamic virtual IP is used in a policy, the dynamic DNS translation table is installed along with the dynamic NAT translation table into the kernel. All matched DNS responses will be translated and recorded regardless if they hit the policy. When a client request hits the policy, dynamic NAT translation will occur if it matches a record, otherwise the traffic will be blocked.
Syntax
config firewall vip
edit 1
set type dns-translation
set extip 192.168.0.1-192.168.0.100
set extintf dmz
set dns-mapping-ttl 604800
set mappedip 3.3.3.0/24 4.0.0.0/24
end
end
GTP Rate Limiting
New methods of GPRS Tunneling Protocol (GTP) rate limiting are available in FortiOS 5.2.
Per-Stream Rate Limiting
FortiOS 5.2 supports per-stream rate limiting of GTP and the ability to apply rate limiting separately for GTPv0 and GTPv1, as well as for GTPv2.
This feature required the addition of the following CLI commands: message-rate-limit-v0, message-rate-limit-v1, and message-rate-limit-v2. The commands message-rate-limit-v0 and message-rate-limit-v1 are only visible when rate-limit-mode is set to per-stream, while message-rate-limit is visible when rate-limit-mode is set to per-profile. The command message-rate-limit-v2 is always visible, since GTPv2 message numbering and naming are different from GTPv0/v1.
The following features have also been added:
- Warning limit support.
- Per-version message rate limiting.
- A log for rate limiting warning called
rate-limited-warning.
In addition, FortiOS Carrier now indicates the GTP version in rate limiting log messages and writes a rate limiting warning log message when a packet exceeds the rate limiting threshold.
Syntax
config firewall gtp
edit <name>
set rate-limit-mode {per-profile | per-stream}
set warning-threshold {0-99}
config {message-rate-limit-v0 | message-rate-limit-v1 | message-rate-limit-v2}
set create-pdp-request <rate-limit>
set delete-pdp-request <rate-limit>
set echo-request <rate-limit>
end
end
Per-APN Rate Limiting Profiles
In FortiOS 5.2, GTP rate limiting profiles can be based per-APN, as well as per-IP. To use this feature, the rate limit for each specific APN needs to be configured in the CLI, as there is no default rate limit.
Syntax
config firewall gtp profile
set rate-limit-mode per-apn
config per-apn-shaper
edit <ID>
set apn <string>
set version <version>
set rate-limit <rate-limit>
end
end
Object UUID Support
|
|
UUID is only supported on large-partition platforms (>=128M). |
A Universally Unique Identified (UUID) attribute has been added to some firewall objects, including virtual IPs and virtual IP groups for IPv4, IPv6, NAT46, and NAT64, so that the logs can record these UUID to be used by a FortiManager or FortiAnalyzer unit.
The UUID of an object can either be generated automatically or assigned through the CLI. To view the UUID for these objects in a FortiGate unit's logs, log-uuid must be set to extended mode, rather than policy-only, which only shows the policy UUID in a traffic log.
Syntax
config sys global
set log-uuid {disable | policy-only | extended}
end
config firewall {policy | policy6 | policy46 | policy64 | address| addres6 | addgrp | addgrp6}
edit <1>
set uuid <8289ef80-f879-51e2-20dd-fa62c5c51f44>
end
end
Configuring the Class of Service Bit
FortiGate units can now configure the value of the Class of Service (CoS) bit, also called Priority Code Point (PCP).
The value of CoS in forward direction (fwd) and reverse direction (rev) is set in the policy/policy6 table using the CLI. The value can be set either as 255, to allow passthrough, or given a priority between 0 and 7.
Syntax
config firewall {policy | policy6}
set vlan-cos-fwd <int>
set vlan-cos-rev <int>
end
Hairpinning for NAT64 and NAT46
In FortiOS 5.2, NAT64 and NAT46 support hairpinning between hosts that are located in the same network behind a single external IP address. Hairpinning allows endpoints on the internal network to communicate using external IP addresses and ports.
In order to allow hairpinning, set permit-any-host must be enabled in the NAT64 or NAT46 firewall policy.
Maximum Number of Available Virtual IPs Increased
The maximum limit of available virtual IPs has been increased on 1U FortiGate models (FortiGate-100 to 800 series) to 16,000 and on 2U FortiGate models (FortiGate-1000 to 3810 series) to 32,000.

