Troubleshooting and logging
This section explains how to troubleshoot logging configuration issues, as well as connection issues, that you may have with your FortiGate unit and a log device. This section also contains information about how to use log messages when troubleshooting issues that are about other FortiGate features, such as VPN tunnel errors.
Using log messages to help in troubleshooting issues
Log messages can help when troubleshooting issues that occur, since they can provide details about what is occurring. The uses and methods for involving logging in troubleshooting vary depending on the problem. The following are examples of how log messages can assist when troubleshooting networking issues.
Using IPS packet logging in diagnostics
This type of logging should only be enabled when you need to know about specific diagnostic information, for example, when you suspect a signature is triggered by a false positive. These log messages can help troubleshoot individual problems with misidentified or missing packets and network intrusions involving malicious packets.
To configure IPS packet logging
- Go to Security Profiles > Intrusion Protection.
- Select the IPS sensor that you want to enable IPS packet logging on, and then select Edit.
- In the filter options, enable Packet Logging.
- Select OK.
If you want to configure the packet quota, number of packets that are recorded before alerts and after attacks, use the following procedure.
To configure additional settings for IPS packet logging
- Log in to the CLI.
- Enter the following to start configuring additional settings:
config ips settings
set ips-packet-quota <integer>
set packet-log-history <integer>
set packet-log-post-attack <integer>
end
Using HA log messages to determine system status
When the FortiGate unit is in HA mode, you may see the following log message content within the event log:
type=event subtype=ha level=critical msg= “HA slave heartbeat interface internal lost neighbor information”
OR
type=event subtype=ha level=critical msg= “Virtual cluster 1 of group 0 detected new joined HA member”
OR
type=event subtype=ha level=critical msg= “HA master heartbeat interface internal get peer information”
The log messages occur within a given time, and indicate that the units within the cluster are not aware of each other anymore. These log messages provide the information you need to fix the problem.
Connection issues between FortiGate unit and logging devices
If external logging devices are not recording the log information properly or at all, the problem will likely be due to one of two situations: no data is being received because the log device cannot be reached, or no data is being sent because the FortiGate unit is no longer logging properly.
Unable to connect to a supported log device
After configuring logging to a supported log device, and testing the connection, you may find you cannot connect. To determine whether this is the problem:
- Verify that the information you entered is correct; it could be a simple mistake within the IP address or you may have not selected Apply on the Log Settings page after changing them, which would prevent them from taking effect.
- Use
execute pingto see if you can ping to the log device. - If you are unable to ping to the log device, check to see if the log device itself working and that it is on the network and assigned an appropriate address.
FortiGate unit has stopped logging
If the FortiGate unit stopped logging to a device, test the connection between both the FortiGate unit and device using the execute ping command. The log device may have been turned off, is upgrading to a new firmware version, or just not working properly.
The FortiGate unit may also have a corrupted log database. When you log into the web-based manager and you see an SQL database error message, it is because the SQL database has become corrupted. View "SQL database errors” in the next section before taking any further actions, to avoid losing your current logs.
Log database issues
If attempting to troubleshoot issues with the SQL log database, use the following to help guide you to solving issues that occur.
SQL statement syntax errors
There may be errors or inconsistencies in the SQL used to maintain the database. Here are some example error messages and possible causes:
You have an error in your SQL syntax (remote/MySQL)
or
ERROR: syntax error at or near... (local/PostgreSQL)
- Verify that the SQL keywords are spelled correctly, and that the query is well-formed.
- Table and column names are demarked by grave accent (`) characters. Single (') and double (") quotation marks will cause an error.
No data is covered.
- The query is correctly formed, but no data has been logged for the log type. Verify that you have configured the FortiGate unit to save that log type. On the Log Settings page, make sure that the log type is checked.
Connection problems
If well-formed SQL queries do not produce results, and logging is turned on for the log type, there may be a database configuration problem with the remote database.
Ensure that:
- MySQL is running and using the default port 3306.
- You have created an empty database and a user who has read/write permissions for the database.
- Here is an example of creating a new MySQL database named fazlogs, and adding a user for the database:
#Mysql –u root –pmysql>Create database fazlogs;mysql>Grant all privileges on fazlogs.* to ‘fazlogger’@’*’ identified by ‘fazpassword’;mysql>Grant all privileges on fazlogs.* to ‘fazlogger’@’localhost’ identified by ‘fazpassword’;
SQL database errors
If the database seems inacessible, you may encounter the following error message after upgrading or downgrading the FortiGate unit’s firmware image.
Example of an SQL database error message
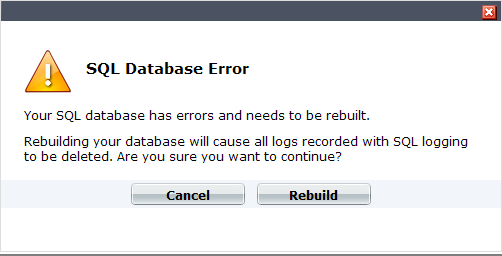
The error message indicates that the SQL database is corrupted and cannot be updated with the SQL schemas any more. When you see this error message, you can do one of the following:
- select Cancel and back up all log files; then select Rebuild to blank and rebuild the database.
- select Rebuild immediately, which will blank the database and previous logs will be lost.
Until the database is rebuilt, no information will be logged by the FortiGate unit regardless of the log settings that are configured on the unit. When you select Rebuild, all logs are lost because the SQL database is erased and then rebuilt again. Logging resumes automatically according to your settings after the SQL database is rebuilt.
To view the status of the database, use the diagnose debug sqldb-error status command in the CLI. This command will inform you whether the database has errors present.
If you want to view the database’s errors, use the diagnose debug sqldb-error read command in the CLI. This command indicates exactly what errors occurred, and what tables contain those errors.
Log files are backed up using the execute backup {disk | memory } {alllogs | logs} command in the CLI. You must use the text variable when backing up log files because the text variable allows you to view the log files outside the FortiGate unit. When you back up log files, you are really just copying the log files from the database to a specified location, such as a TFTP server.
Logging daemon (Miglogd)
The number of logging daemon child processes has been made available for editing. A higher number can affect performance, and a lower number can affect log processing time, although no logs will be dropped or lost if the number is decreased.
If you are suffering from performance issues, you can alter the number of logging daemon child processes, from 0 to 15, using the following syntax. The default is 8.
config system global
set miglogd-children <integer>
end

