4. Configure these settings: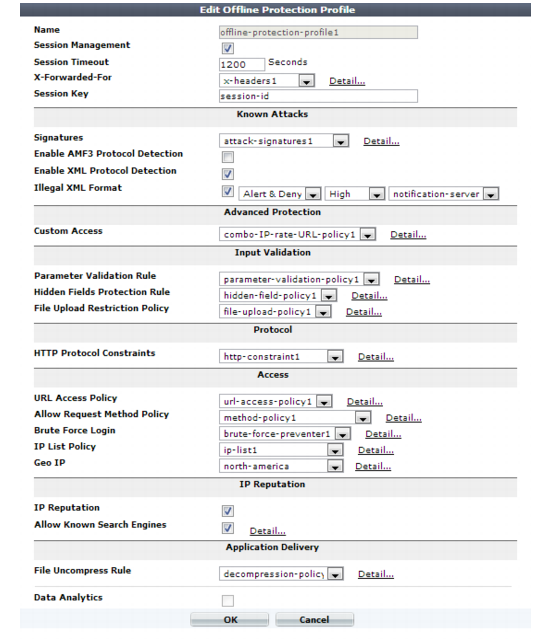

Offline protection profiles only include features that do not require an inline network topology. You can configure them at any time, but a policy cannot apply an offline protection profile if the FortiWeb appliance is operating in a mode that does not support them. For details, see Table 47. |
To save time, you may be able to use auto-learning to generate protection profiles and their components by observing your web servers’ traffic. For details, see “Auto-learning”. |

Setting name | Description |
Name | Type a unique name that can be referenced in other parts of the configuration. Do not use spaces or special characters. The maximum length is 35 characters. |
Session Management | Enable to use your web application’s session IDs in order for FortiWeb to be able to track the state of web applications across multiple requests. Also configure Session Timeout. Note: When FortiWeb is deployed in an offline topology or asynchronous operation mode, this feature requires that your web applications have session IDs in their URL. For details, see “HTTP sessions & security” and “Supported features in each operation mode”. Note: Enabling this option is required if: • you select features requiring session cookies, such as Hidden Fields Protection Rule • in any policy, you will select an auto-learning profile with this profile • you want to include this profile’s traffic in the traffic log |
Session Timeout | Type the HTTP session timeout in seconds. After this time elapses during which there were no more subsequent requests, after which the FortiWeb appliance will regard the next request as the start of a new HTTP session. This option appears only if Session Management is enabled. The default is 1200 (20 minutes). The valid range is from 20 to 3,600 seconds. |
Session Key | Type the name of the session ID, if any, that your web application uses in the URL to identify each session. By default, FortiWeb tracks some common session ID names: ASPSESSIONID, PHPSESSIONID, and JSESSIONID. Configure this field if your web application uses a custom or uncommon session ID. In those cases, you do not need to configure this setting. For example, in the following URL, a web application identifies its sessions using a parameter with the name mysession: page.php?mysession=123ABC&user=user1 In that case, you must configure Session Key to be mysession so that FortiWeb will be able to recognize the session ID, 123ABC, and apply features that require sessions in order to function. This option appears only if Session Management is enabled. |
Signature | Select the name of the signature set, if any, that will be applied to matching requests. Attack log messages for this feature vary by which type of attack was detected. For a list, see “Blocking known attacks & data leaks”. Note: If a WAF Auto Learning Profile will be selected in the policy with this profile, you should select a signature set whose Action is Alert. If the Action is Alert & Deny, the FortiWeb appliance will reset the connection when it detects an attack, resulting in incomplete session information for the auto-learning feature. |
Enable AMF3 Protocol Detection | Enable to scan requests that use action message format 3.0 (AMF3) for: • cross-site scripting (XSS) attacks • SQL injection attacks • common exploits and other attack signatures that you have enabled in Signature. AMF3 is a binary format that can be used by Adobe Flash/Flex clients to send input to server-side software. Caution: To scan for attacks or enforce input rules on AMF3, you must enable this option. Failure to enable the option will cause the FortiWeb appliance to be unable to scan AMF3 requests for attacks. |
Enable XML Protocol Detection | Enable to scan for matches with attack and data leak signatures in Web 2.0 (XML AJAX) and other XML submitted by clients in the bodies of HTTP POST requests. |
Illegal XML Format | Enable to validate that XML elements and attributes in the request’s body conforms to the W3C XML 1.1 and/or XML 2.0 standards. Malformed XML, such as without the final > or with multiple >> in the closing tag, is often an attempt to exploit an unhandled error condition in a web application’s XHTML or XML parser. Attack log messages contain Illegal XML Format when this feature detects malformed XML. |
Custom Rule | Select the name of a combination source IP, rate limit, HTTP header, and URL access policy, if any, that is applied to matching requests. See “Combination access control & rate limiting”. Attack log messages contain Advanced Protection Violation when this feature detects a violation. |
Padding Oracle Protection | Select the name of padding oracle protection rule, if any, that will be applied to matching requests. See “Defeating cipher padding attacks on individually encrypted inputs”. Attack log messages contain Padding Oracle Attack when this feature detects a violation. |
Parameter Validation Rule | Select the name of the HTTP parameter validation rule, if any, that will be applied to matching requests. See “Validating parameters (“input rules”)”. Attack log messages contain Parameter Validation Violation when this feature detects a parameter rule violation. Note: If a WAF Auto Learning Profile will be selected in a server policy using this profile, you should select a parameter validation rule whose Action is Alert. If the Action is Alert & Deny, the FortiWeb appliance will reset the connection when it detects an attack, resulting in incomplete session information for the auto-learning feature. |
Hidden Fields Protection Rule | Select the name of a hidden fields group, if any, that will be applied to matching requests. See “Preventing tampering with hidden inputs”. Attack log messages contain Hidden Field Manipulation when this feature detects hidden input tampering. This option appears only if Session Management is enabled. |
File Upload Restriction Policy | Select an existing file upload restriction policy, if any, that will be applied to matching requests. See “Limiting file uploads”. Attack log messages contain Illegal file size when this feature detects an excessively large upload. |
HTTP Protocol Constraints | Select the name of an HTTP protocol constraint, if any, that will be applied to matching requests. See “HTTP/HTTPS protocol constraints”. Attack log messages for this feature vary by which type of attack was detected. For a list, see “HTTP/HTTPS protocol constraints”. |
URL Access Policy | Select the name of the URL access policy, if any, that will be applied to matching requests. See “Restricting access to specific URLs”. Attack log messages contain URL Access Violation when this feature detects a request that violates this policy. Note: Do not select an URL access policy if this offline protection profile will be used in a policy with WAF Auto Learning Profile. Selecting an URL access policy will cause the FortiWeb appliance to reset the connection when it detects a request with a blocked URL and Host: field combination, resulting in incomplete session information for the auto-learning feature. |
Allow Request Method Policy | Select an existing allowed method policy, if any, that will be applied to matching requests. See “Specifying allowed HTTP methods”. Attack log messages contain HTTP Method Violation when this feature detects a non-allowed HTTP request method. Note: If a WAF Auto Learning Profile will be selected in a server policy using this profile, you must enable the HTTP request methods that will be used by sessions that you want the FortiWeb appliance to learn about. If a method is disabled, the FortiWeb appliance will reset the connection, and therefore cannot learn about the session. |
Brute Force Login | Select the name of a brute force login attack profile, if any, that will be applied to matching requests. See “Preventing brute force logins”. Attack log messages contain Brute Force Login Violation when this feature detects a brute force login attack. |
IP List Policy | Select the name of a client black list or white list, if any, that will be applied to matching requests. See “Blacklisting & whitelisting clients using a source IP or source IP range”. Attack log messages contain Blacklisted IP blocked when this feature detects a blacklisted source IP address. |
Geo IP | Select the name of a geographically-based client black list, if any, that will be applied to matching requests. See “Blacklisting & whitelisting countries & regions”. |
IP Reputation | Enable to apply IP reputation-based blacklisting. See “Blacklisting source IPs with poor reputation”. |
Allow Known Search Engines | Enable to exempt popular search engines’ spiders from DoS sensors, brute force login sensors, HTTP protocol constraints, and combination rate & access control (called “advanced protection” and “custom policies” in the web UI). This option improves access for search engines. Rapid access rates, unusual HTTP usage, and other characteristics that may be abnormal for web browsers are often normal with search engines. If you block them, your web sites’ rankings and visibility may be affected. By default, this option allows all popular predefined search engines. To specify which search engines will be exempt, click the Details link. A new frame will appear on the right side of the protection profile. Enable or disable each search engine, then click Apply. See also “Blacklisting content scrapers, search engines, web crawlers, & other robots”. |
File Uncompress Rule | Select the name of a file decompression policy, if any, that will be applied to matching requests. See “Configuring temporary decompression for scanning & rewriting”. |
Data Analytics | Enable to gather hit, attack, and traffic volume statistics for each server policy that includes this profile. See “Configuring policies to gather data” and “Viewing web site statistics”. Note: This option cannot be enabled until you have uploaded a geography-to-IP mapping database. See “Updating data analytics definitions”. |