Blacklisting source IPs with poor reputation
Manually identifying and blocking all known attackers in the world would be an impossible task. To block:
• botnets
• spammers
• phishers
• malicious spiders/crawlers
• virus-infected clients
• clients using anonymizing proxies
• DDoS participants
you can configure FortiWeb to use the FortiGuard IP Reputation. IP reputation leverages many techniques for accurate, early, and frequently updated identification of compromised and malicious clients so you can block attackers before they target your servers. Data about dangerous clients derives from many sources around the globe, including:
• FortiGuard service statistics
• honeypots
• botnet forensic analysis
• anonymizing proxies
• 3rd-party sources in the security community
From these sources, Fortinet compiles a reputation for each public IP address. Clients will have poor reputations if they have been participating in attacks, willingly or otherwise. Because blacklisting innocent clients is equally undesirable, Fortinet also restores the reputations of clients that improve their behavior. This is crucial when an infected computer is cleaned, or in DHCP or PPPoE pools where an innocent client receives an IP address that was previously leased by an attacker.
| Because IP reputation data is based on evidence of hostility rather than a client’s current physical location on the globe, if your goal is to block attackers rather than restrict delivery, this feature may be preferable. |
IP reputation knowledge is regularly updated if you have subscribed and connected your FortiWeb to the FortiGuard IP Reputation service (see
“Connecting to FortiGuard services”). Due to this, new options will periodically appear. You can monitor the
FortiGuard web site feed for security advisories which may correlate with new IP reputation-related options.
| Because geographical IP policies are evaluated before many other techniques, defining these IP addresses can be used to improve performance. For details, see “Sequence of scans”. |
To configure the policy
1. If you need to exempt some clients’ public IP addresses due to possible false positives, configure IP reputation exemptions first. Go to IP Reputation > IP Reputation > Exceptions.
2. Go to
IP Reputation > IP Reputation > Policy.
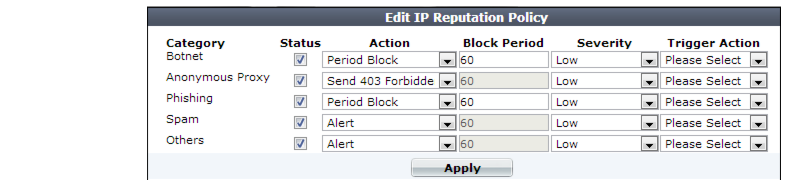
3. In the Status column, enable categories of disreputable clients that you want to block and/or log.
| APTs often mask their source IP using anonymizing proxies. While casual attackers will move on to easier potential targets if their initial attempts fail, APTs are motivated to persist until they achieve a successful breach. Early warning can be critical. Therefore even if some innocent anonymous clients use your web servers and you do not want to block them, you still may want to log proxied anonymous requests. Filtering your other attack logs by these anonymous IPs can help you to locate and focus on dangerous requests from these IPs, whether you want to use them to configure a defense, for law enforcement, or for forensic analysis. |
5. Click Apply.
Attack log messages contain Anonymous Proxy : IP Reputation Violation or Botnet : IP Reputation Violation when this feature detects a possible attack.
See also


