Scheduling automatic signature updates
Your FortiWeb appliance uses signatures, IP lists, and data type definitions for many features, including to detect attacks such as:
• cross-site scripting (XSS)
• SQL injection
• other common exploits
• data leaks
FortiWeb also can use virus definitions to block trojan uploads, and can use IP reputation definitions to allow search engines but block botnets and anonymizing proxies preferred by hackers. FortiGuard services ensure that your FortiWeb is using the most advanced attack protections. Timely updates are crucial to defending your network.
You can configure the FortiWeb appliance to periodically poll for FortiGuard service updates from the FDN, and automatically download and apply updates if they exist.
For example, you might schedule update requests every night at 2 AM local time, when traffic volume is light.
To configure automatic updates
2. Go to System > Config > FortiGuard.
To access this part of the web UI, your administrator's account access profile must have
Read and
Write permission to items in the
Maintenance category. For details, see
“Permissions”.
The page informs you if you are not registered or if registration has expired. If your registration is active, continue scheduling updates; otherwise, click Register or Renew.
3. Enable Scheduled Update.
4. Select either:
• Every — Select to request to update once every 1 to 23 hours, then select the number of hours between each update request.
• Daily — Select to update once every day, then select the hour. The update attempt occurs at a randomly determined time within the selected hour.
• Weekly — Select to request to update once a week, then select the day of the week, the hour, and the minute of the day to check for updates.
If you select
00 minutes, the update request occurs at a randomly determined time within the selected hour.
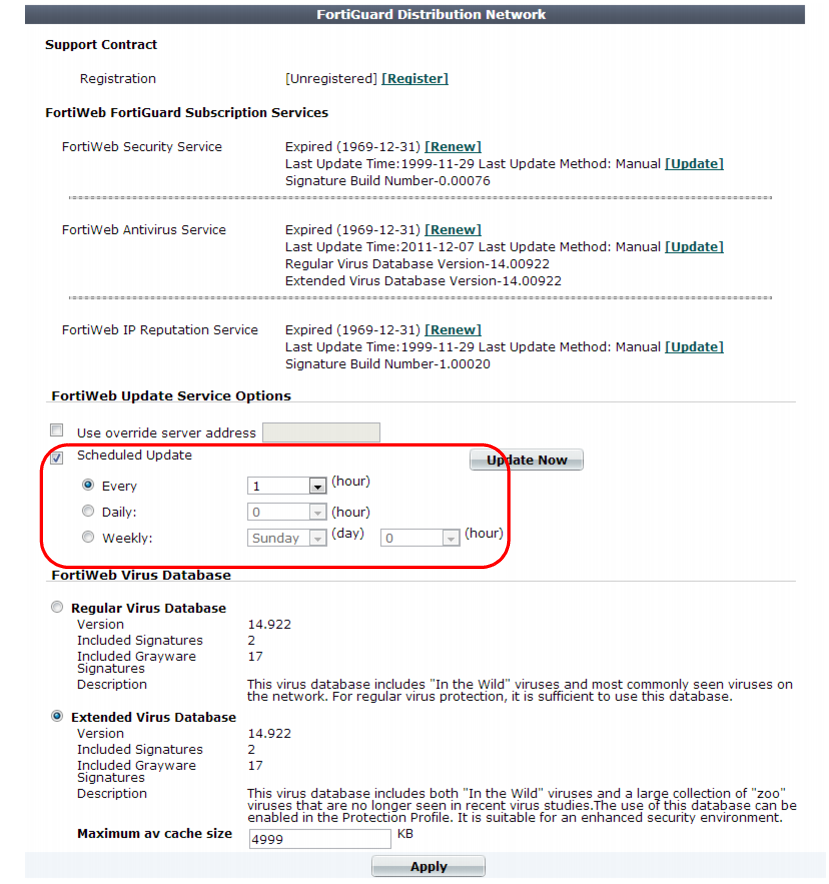
5. Click Apply.
The FortiWeb appliance next requests an update according to the schedule.
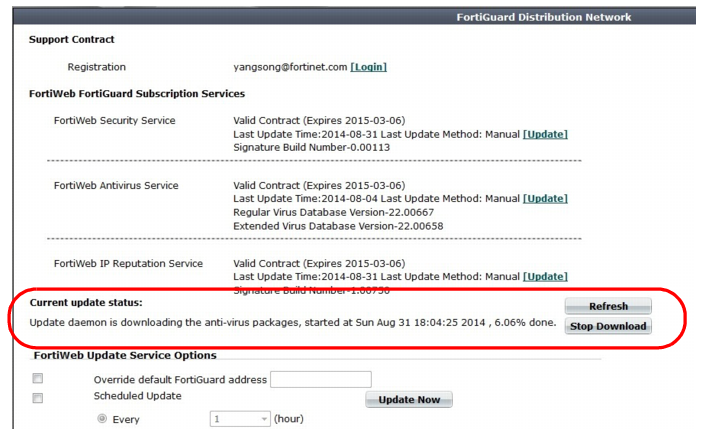
At the scheduled time, FortiWeb starts the update. Under Current update status, the following information is displayed:
• The name of the update package that is currently downloading, the start time of the download operation, and the percentage complete.
• A Refresh button, which allows you to update the package download status information.
• If FortiWeb is downloading an anti-virus package, a Stop button.
This option is useful if, for example, the download is slow and you want to stop it and try again later. It can also be useful if you want to stop the scheduled update and instead update your anti-virus package using a file you have manually downloaded from the Fortinet Technical Support web site (
“Uploading signature & geography-to-IP updates”.)
Results of the update activity appear in FortiWeb Security Service in the FortiGuard Information widget. If you have enabled logging in:
• Log & Report > Log Config > Other Log Settings
• Log & Report > Log Config > Global Log Settings
when the FortiWeb appliance requests an update, the event is recorded in Log & Report > Log Access > Event, such as these log message:
FortiWeb virus signature is already up-to-date
FortiWeb IP reputation signature update succeeded
If the FortiWeb appliance cannot successfully connect, it records a log with a message that varies by the cause of the error, such as:
FortiWeb is unauthorized.
Once the attack signature update is complete, FortiWeb immediately begins to use them. No reboot is required.
See also



