Configuring RADIUS queries
FortiWeb can use RADIUS queries to authenticate and authorize end-users’ HTTP requests (see
“Offloading HTTP authentication & authorization”). FortiWeb can also use RADIUS queries to authenticate administrators’ access to the web UI or CLI (see
“Grouping remote authentication queries for administrators”).
| If you use a RADIUS query for administrators, separate it from the queries for regular users. Do not combine administrator and user queries into a single entry. Failure to separate queries will allow end-users to have administrative access the FortiWeb web UI and CLI. |
Remote Authentication and Dial-in User Service (RADIUS) servers provide authentication, authorization, and accounting functions. The FortiWeb authentication feature uses RADIUS user queries to authenticate and authorize HTTP requests. (The HTTP protocol does not support active logouts, and can only passively log out users when their connection times out. Therefore FortiWeb does not fully support RADIUS accounting.) RADIUS authentication with realms (i.e. the person logs in with an account such as admin@example.com) are supported.
To authenticate a user or administrator, the FortiWeb appliance sends the user’s credentials to RADIUS for authentication. If the RADIUS server replies to the query with a signal of successful authentication, the client is successfully authenticated with the FortiWeb appliance. If RADIUS authentication fails or the query returns a negative result, the appliance refuses the connection.
If this query will be used to authenticate administrators, and your RADIUS server is slow to answer, you may need to adjust the authentication timeout setting to prevent the query from failing. See the
FortiWeb CLI Reference. (For end-user queries, configure
Connection Timeout instead.)
To configure a RADIUS query
1. Before configuring the query, if you will configure a secure connection, you must upload the certificate of the CA that signed the RADIUS server’s certificate. For details, see
“Uploading trusted CAs’ certificates”.
2. Go to User > Remote Server > RADIUS Server.
To access this part of the web UI, your administrator's account access profile must have
Read and
Write permission to items in the
Auth Users category. For details, see
“Permissions”.
3. Click Create New.
A dialog appears.
4. Configure these settings:
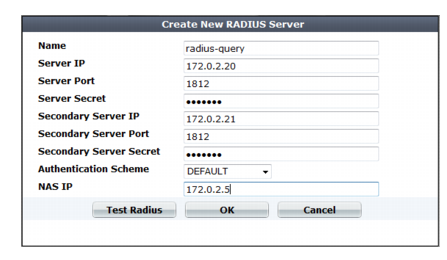
Setting name | Description |
Name | Type a unique name that can be referenced in other parts of the configuration. Do not use spaces or special characters. The maximum length is 35 characters. Note: This is the name of the query only, not the administrator or end-user’s account name/login. Administrator account names are defined in Administrator. End-user names are not defined in the configuration; credentials provided by the person during login will be used for the query. |
Server IP | Type the IP address of the primary RADIUS server. |
Server Port | Type the port number where the RADIUS server listens. The default port number is 1812. |
Server Secret | Type the RADIUS server secret key for the primary RADIUS server. The primary server secret key should be a maximum of 16 characters in length. |
Secondary Server IP | Type the IP address of the secondary RADIUS server, if applicable. |
Secondary Server Port | Type the port number where the RADIUS server listens. The default port number is 1812. |
Secondary Server Secret | Type the RADIUS server secret key for the secondary RADIUS server. The secondary server secret key should be a maximum of 16 characters in length. |
Authentication Scheme | Select either: • Default to authenticate with the default method. The default authentication scheme uses PAP, MS-CHAP-V2, and CHAP, in that order. • MS-CHAP-V2, CHAP, MS-CHAP, or PAP, depending on what your RADIUS server requires. |
NAS IP | Type the NAS IP address and Called Station ID (for more information about RADIUS Attribute 31, see RFC 2548 Microsoft Vendor-specific RADIUS Attributes). If you do not enter an IP address, the IP address that the FortiWeb appliance uses to communicate with the RADIUS server will be applied. |
5. Click OK.
6. Return to User > Remote Server > LDAP User, double-click the row of the query, then click the Test RADIUS button to verify that FortiWeb can connect to the server, and that the query is correctly configured.
If the query is for
user accounts that you want to allow to authenticate with web servers, to activate the user account, you must indirectly include it in a server policy. Continue with
“Grouping users”. (For an overview, see
“To configure and activate end-user accounts”.)
See also


