A dialog appears.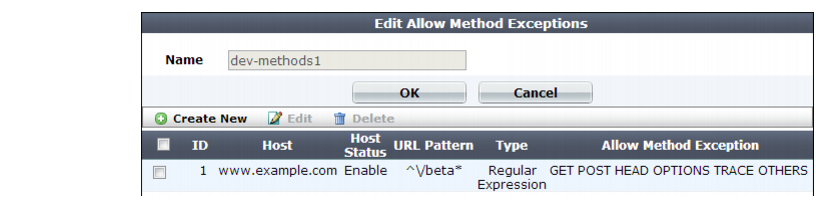


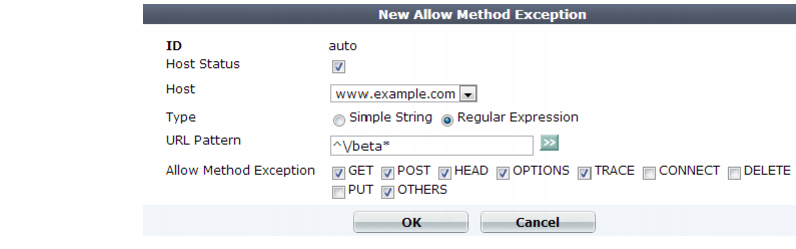
Setting name | Description |
Host Status | Enable to require that the Host: field of the HTTP request match a protected host names entry in order to match the allowed method exception. Also configure Host. |
Host | Select which protected host names entry (either a web host name or IP address) that the Host: field of the HTTP request must be in to match the allowed method exception. This option is available only if Host Status is enabled. |
Type | Select whether URL Pattern is a Simple String (that is, a literal URL) or a Regular Expression. |
URL Pattern | Depending on your selection in Type, enter either: • the literal URL, such as /index.php, that is an exception to the generally allowed HTTP request methods. The URL must begin with a slash ( / ). • a regular expression, such as ^/*.php, matching all and only the URLs which are exceptions to the generally allowed HTTP request methods. The pattern does not require a slash ( / ); however, it must at match URLs that begin with a slash, such as /index.cfm. For example, if multiple URLs on a host have identical HTTP request method requirements, you would type a regular expression matching all of and only those URLs. Do not include the domain name, such as www.example.com, which is configured separately in the Host drop-down list. To create and test a regular expression, click the >> (test) icon. This opens the Regular Expression Validator window where you can fine-tune the expression (see “Regular expression syntax”). |
Allow Method Exception | Mark the check boxes of all HTTP request methods that you want to allow. Methods that you do not select will be denied. The OTHERS option includes methods not specifically named in the other options. It often may be required by WebDAV (RFC 4918) applications such as Microsoft Exchange Server 2003 and Subversion, which may require HTTP methods not commonly used by web browsers, such as PROPFIND and BCOPY. Note: If a WAF Auto Learning Profile will be selected in the policy with an offline protection profile that uses this allowed method exception, you must enable the HTTP request methods that will be used by sessions that you want the FortiWeb appliance to learn about. If a method is disabled, the FortiWeb appliance will reset the connection, and therefore cannot learn about the session. |