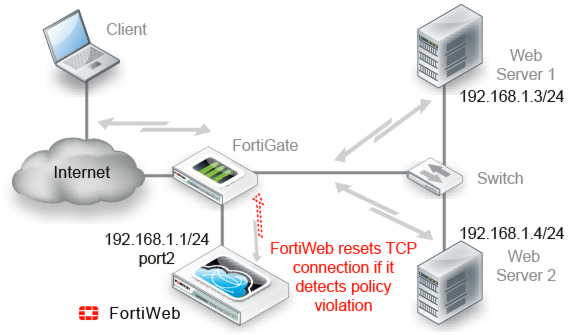
Topology for offline protection mode
“Out-of-band” is an appropriate descriptor for this mode. Minimal changes are required. It does not introduce any latency. However, many features are not supported (see
“Supported features in each operation mode”).
| Most organizations do not permanently deploy their FortiWeb in offline protection mode. Instead, they will use it as a way to learn about their web servers’ vulnerabilities and to configure some of the FortiWeb during a transition period, after which they will switch to an operation mode that places the appliance inline (between clients and web servers). Switching out of offline protection mode when you are done with transition can prevent bypass problems that can arise as a result of misconfigured routing. It also offers you the ability to offer protection features that cannot be supported in a SPAN port topology. |
Requests are destined for a web server, not the FortiWeb appliance. Traffic is duplicated from the flow and sent on an out-of-line link to the FortiWeb through a switched port analyzer (SPAN or mirroring) port. Unless there is a policy violation, there is no reply traffic from FortiWeb. Depending on whether the upstream firewalls or routers apply source NAT (SNAT), the web servers might be able to see and use the source IP addresses of clients.
FortiWeb monitors traffic received on the data capture port’s network interface (regardless of the IP address) and applies the first applicable policy. Because it is not inline with the destination, it does not forward permitted traffic. FortiWeb logs or blocks violations according to the matching policy and its protection profile. If FortiWeb detects a malicious request, it sends a TCP RST (reset) packet through the blocking port to the web server and client to attempt to terminate the connection. It does not otherwise modify traffic. (It cannot, for example, offload SSL, load-balance connections, or support user authentication.)
| Unlike in reverse proxy mode or true transparent proxy mode, actions other than Alert cannot be guaranteed to be successful in offline protection mode. The FortiWeb appliance will attempt to block traffic that violates the policy by mimicking the client or server and requesting to reset the connection. However, the client or server may receive the reset request after it receives the other traffic due to possible differences in routing path metrics and latency. |
Figure 16 shows an example one-arm network topology for offline protection mode. A client accesses two web servers over the Internet through a FortiWeb appliance. A firewall is installed between the FortiWeb appliance and the Internet to regulate non-HTTP/HTTPS traffic. Port1 is connected to the administrator’s computer. Port2 is connected to the firewall, and thereby to a switch, which is connected to the web servers. The FortiWeb appliance provides detection, but does not load-balance, block, or otherwise modify traffic to or from the two web servers.