Administrative domains (ADOMs)
Administrative domains (ADOMs) enable the admin administrator to constrain other FortiWeb administrators’ access privileges to a subset of policies and protected host names. This can be useful for large enterprises and multi-tenant deployments such as web hosting.
ADOMs are not enabled by default. Enabling and configuring administrative domains can only be performed by the admin administrator.
Enabling ADOMs alters the structure of and the available functions in the GUI and CLI, according to whether or not you are logging in as the admin administrator, and, if you are not logging in as the admin administrator, the administrator account’s assigned access profile.
Table 4: Differences between administrator accounts when ADOMs are enabled
| admin administrator account | Other administrators |
Acess to config global | Yes | No |
Can create administator accounts | Yes | No |
Can create & enter all ADOMs | Yes | No |
• If ADOMs are enabled and you log in as admin, a superset of the typical CLI commands appear, allowing unrestricted access and ADOM configuration.
config global contains settings used by the FortiWeb itself and settings shared by ADOMs, such as RAID and administrator accounts. It does not include ADOM-specific settings or data, such as logs and reports. When configuring other administrator accounts, an additional option appears allowing you to restrict other administrators to an ADOM.
• If ADOMs are enabled and you log in as any other administrator, you enter the ADOM assigned to your account. A subset of the typical menus or CLI commands appear, allowing access only to only logs, reports, policies, servers, and LDAP queries specific to your ADOM. You cannot access global configuration settings, or enter other ADOMs.
By default, administrator accounts other than the admin account are assigned to the root ADOM, which includes all policies and servers. By creating ADOMs that contain a subset of policies and servers, and assigning them to administrator accounts, you can restrict other administrator accounts to a subset of the FortiWeb’s total protected servers.
The admin administrator account cannot be restricted to an ADOM. Other administrators are restricted to their ADOM, and cannot configure ADOMs or global settings.
To enable ADOMs
1. Log in with the admin account.
Other administrators do not have permissions to configure ADOMs.
| Back up your configuration. Enabling ADOMs changes the structure of your configuration, and moves non-global settings to the root ADOM. For information on how to back up the configuration, see “Backups”. |
2. Go to
System > Status > Status, then in the
System Information widget, in the
Administrative Domains row, click
Enable.
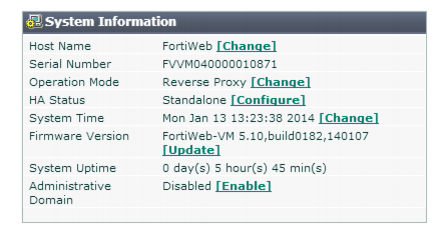
FortiWeb terminates your administrative session.
3. Log in again.
When ADOMs are enabled, and if you log in as
admin, the navigation menu on the left changes: the two top level items are
Global and
Administrative Domain.
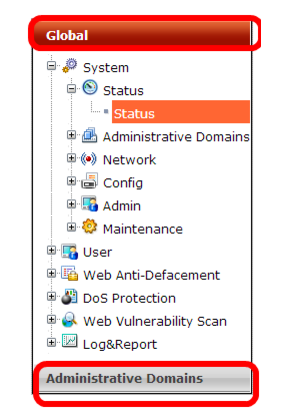
• Global contains settings that only admin or other accounts with the prof_admin access profile can change.
• Administrative Domains contains each ADOM and its respective settings.
This menu and CLI structure change is not visible to non-global accounts; ADOM administrators’ navigation menus continue to appear similar to when ADOMs are disabled, except that global settings such as network interfaces, HA, and other global settings do not appear.
To disable ADOMs
1. Delete all ADOM administrator accounts.
| Back up your configuration. Disabling ADOMs changes the structure of your configuration, and deletes most ADOM-related settings. It keeps settings from the root ADOM only. For information on how to back up the configuration, see “Backups”. |
2. Go to System > Status > Status, then in the System Information widget, in the Administrative Domains row, click Disable.
See also




