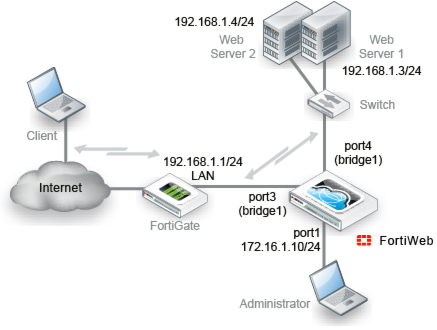
Topology for either of the transparent modes
No changes to the IP address scheme of the network are required. Requests are destined for a web server,
not the FortiWeb appliance. More features are supported than offline protection mode, but fewer than reverse proxy, and may vary if you use HTTPS (see also
“Supported features in each operation mode”).
Unlike with reverse proxy mode, with both transparent modes, web servers will see the source IP address of clients.
You can configure VLAN subinterfaces on FortiWeb, or omit IP address configuration entirely and instead assign a network port to be a part of a Layer 2-only bridge.
Figure 15 shows one example of network topology for either true transparent proxy or transparent inspection mode. A client accesses a web server over the Internet through a FortiWeb appliance. A firewall is installed between the FortiWeb appliance and the Internet to regulate non-HTTP/HTTPS traffic. Port1 is connected to the administrator’s computer. Port3 is connected to the firewall. Port4 is connected to the web servers. Port3 and port4 have no IP address of their own, and act as a V-zone (bridge). Because port3 and port4 have hardware support for fail-to-wire, this topology also gives you the option of configuring fail-open behavior in the event of FortiWeb power loss.
True transparent proxy mode and transparent inspection mode are the same in topology aspect, but due to differences in the mode of interception, they do have a few important behavioral differences:
• True transparent proxy — FortiWeb transparently proxies the traffic arriving on a network port that belongs to a Layer 2 bridge, applies the first applicable policy, and lets permitted traffic pass through. FortiWeb logs, blocks, or modifies violations according to the matching policy and its protection profile. This mode supports user authentication via HTTP but not HTTPS.
• Transparent inspection — FortiWeb asynchronously inspects traffic arriving on a network port that belongs to a Layer 2 bridge, applies the first applicable policy, and lets permitted traffic pass through. (Because it is asynchronous, it minimizes latency.) FortiWeb logs or blocks traffic according to the matching policy and its protection profile, but does not otherwise modify it. (It cannot, for example, offload SSL, load-balance connections, or support user authentication.
| Unlike in reverse proxy mode or true transparent proxy mode, actions other than Alert cannot be guaranteed to be successful in transparent inspection mode. The FortiWeb appliance will attempt to block traffic that violates the policy. However, due to the nature of asynchronous inspection, the client or server may have already received the traffic that violated the policy. |