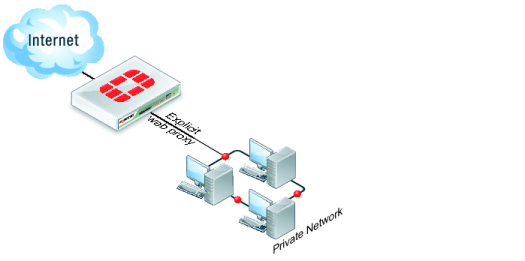
The FortiGate explicit web proxy
You can use the FortiGate explicit web proxy to enable explicit proxying of IPv4 and IPv6 HTTP, and HTTPS traffic one or more FortiGate interfaces. The explicit web proxy also supports proxying FTP sessions from a web browser and proxy auto-config (PAC) to provide automatic proxy configurations for explicit web proxy users. From the CLI you can also configure the explicit web proxy to support SOCKS sessions from a web browser.
The explicit web and FTP proxies can be operating at the same time on the same or on different FortiGate interfaces.
| If explicit web proxy options are not visible on the web‑based manager, go to System > Config > Features and turn on Explicit Proxy. |
In most cases you would configure the explicit web proxy for users on a network by enabling the explicit web proxy on the FortiGate interface connected to that network. Users on the network would configure their web browsers to use a proxy server for HTTP and HTTPS, FTP, or SOCKS and set the proxy server IP address to the IP address of the FortiGate interface connected to their network. Users could also enter the PAC URL into their web browser PAC configuration to automate their web proxy configuration using a PAC file stored on the FortiGate unit.
| Enabling the explicit web proxy on an interface connected to the Internet is a security risk because anyone on the Internet who finds the proxy could use it to hide their source address. |
If the FortiGate unit is operating in Transparent mode, users would configure their browsers to use a proxy server with the FortiGate management IP address.
If the FortiGate unit is operating with multiple VDOMs the explicit web proxy is configured for each VDOM.
The web proxy receives web browser sessions to be proxied at FortiGate interfaces with the explicit web proxy enabled. The web proxy uses FortiGate routing to route sessions through the FortiGate unit to a destination interface. Before a session leaves the exiting interface, the explicit web proxy changes the source addresses of the session packets to the IP address of the exiting interface. When the FortiGate unit is operating in Transparent mode the explicit web proxy changes the source addresses to the management IP address. You can configure the explicit web proxy to keep the original client IP address. See
“Preventing the explicit web proxy from changing source addresses”.
For more information about explicit web proxy sessions, see
“Explicit proxy sessions and user limits”.
To allow all explicit web proxy traffic to pass through the FortiGate unit you can set the explicit web proxy default firewall policy action to accept. However, in most cases you would want to use security policies to control explicit web proxy traffic and apply security features such as access control/authentication, virus scanning, web filtering, application control, and traffic logging. You can do this by keeping the default explicit web proxy security policy action to deny and then adding web-proxy security policies.
You can also change the explicit web proxy default security policy action to accept and add explicit web proxy security policies. If you do this, sessions that match web-proxy security policies are processed according to the security policy settings. Connections to the explicit web proxy that do not match a web‑proxy security policy are allowed with no restrictions or additional security processing. This configuration is not recommended and is not a best practice.
Web-proxy policies can selectively allow or deny traffic, apply authentication, enable traffic logging, and use security profiles to apply virus scanning, web filtering, IPS, application control, DLP, and SSL/SSH inspection to explicit web proxy traffic.
You cannot configure Traffic shaping for explicit web proxy traffic. Web Proxy policies can only include firewall addresses not assigned to a FortiGate unit interface or with interface set to Any. (On the web‑based manager you must set the interface to Any. In the CLI you must unset the associated-interface.)
Authentication of explicit web proxy sessions uses HTTP authentication and can be based on the user’s source IP address or on cookies from the user’s web browser. For more information, see
“Explicit web proxy authentication”.
To use the explicit web proxy, users must add the IP address of a FortiGate interface on which the explicit web proxy is enabled and the explicit web proxy port number (default 8080) to the proxy configuration settings of their web browsers.
On FortiGate units that support it, you can also enable web caching for explicit web proxy sessions.
This section describes: