FortiGate web caching can be added to any security policy and any HTTP or HTTPS traffic accepted by that security policy can be cached on the FortiGate unit hard disk. This includes WAN optimization and explicit web proxy traffic. The network topologies for these scenarios are very similar. They involved a FortiGate unit installed between users and web servers with web caching enabled.
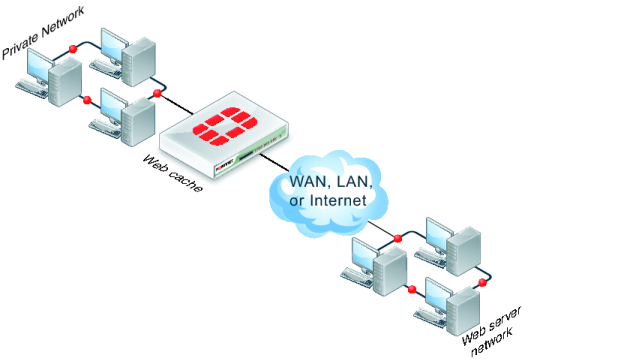
A typical web-caching topology includes one FortiGate unit that acts as a web cache server (
Figure 323). Web caching is enabled in a security policy and the FortiGate unit intercepts web page requests accepted by the security policy, requests web pages from the web servers, caches the web page contents, and returns the web page contents to the users. When the FortiGate unit intercepts subsequent requests for cached web pages, the FortiGate unit contacts the destination web server just to check for changes.
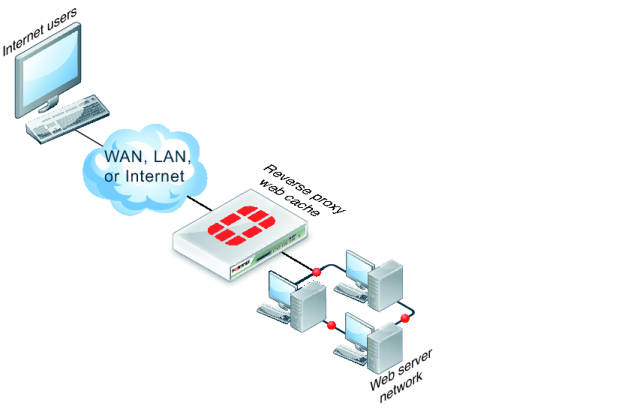
You can also configure reverse proxy web-caching (
Figure 324). In this configuration, users on the Internet browse to a web server installed behind a FortiGate unit. The FortiGate unit intercepts the web traffic (HTTP and HTTPS) and caches pages from the web server. Reverse proxy web caching on the FortiGate unit reduces the number of requests that the web server must handle, leaving it free to process new requests that it has not serviced before.