Different source and destination NAT for SIP and RTP
This is a more complex scenario that a SIP service provider may use. It can also be deployed in large-scale SIP environments where RTP has to be processed by the FortiGate unit and the RTP server IP has to be translated differently than the SIP server IP.
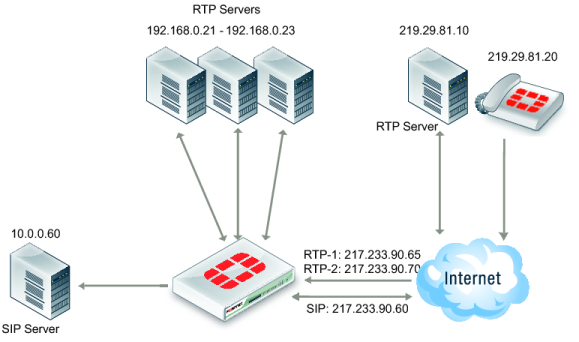
In this scenario, shown in
Figure 301, assume there is a SIP server and a separate media gateway. The SIP server is configured so that the SIP phone (219.29.81.20) will connect to 217.233.90.60. The media gateway (RTP server: 219.29.81.10) will connect to 217.233.90.65.
What happens is as follows:
1. The SIP phone connects to the SIP VIP. The FortiGate ALG translates the SIP contact header to the SIP server: 219.29.81.20 > 217.233.90.60 (> 10.0.0.60).
2. The SIP server carries out RTP to 217.233.90.65.
3. The FortiGate ALG opens pinholes, assuming that it knows the ports to be opened.
4. RTP is sent to the RTP-VIP (217.233.90.65.) The FortiGate ALG translates the SIP contact header to 192.168.0.21.