Destination NAT (SIP and RTP)
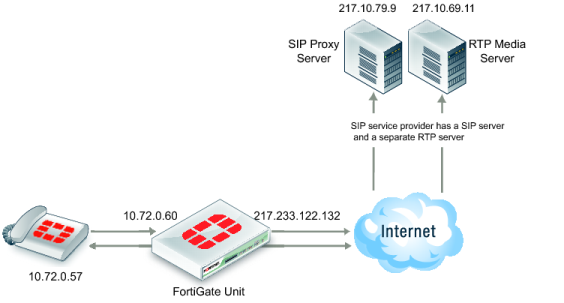
In the following destination NAT scenario, a SIP phone can connect through the FortiGate unit to private IP address using a firewall virtual IP (VIP). The SIP ALG translates the SIP contact header to the IP of the real SIP proxy server located on the Internet.
In the scenario, shown in
Figure 299, the SIP phone connects to a VIP (10.72.0.60). The SIP ALG translates the SIP contact header to 217.10.79.9, opens RTP pinholes, and manages NAT.
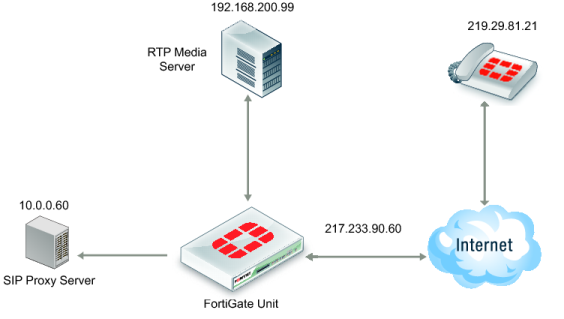
The FortiGate unit also supports a variation of this scenario where the RTP media server’s IP address is hidden on a private network or DMZ.
In the scenario shown in
Figure 300, a SIP phone connects to the Internet. The VoIP service provider only publishes a single public IP. The FortiGate unit is configured with a firewall VIP. The SIP phone connects to the FortiGate unit (217.233.90.60) and using the VIP the FortiGate unit translates the SIP contact header to the SIP proxy server IP address (10.0.0.60). The SIP proxy server changes the SIP/SDP connection information (which tells the SIP phone which RTP media server IP it should contact) also to 217.233.90.60.