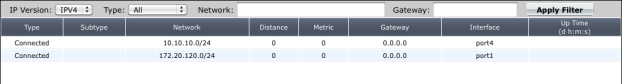
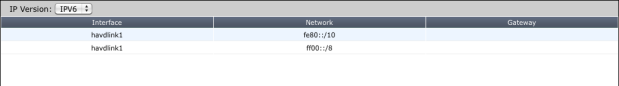
IP version: | Select IPv4 or IPv6. This is available only when IPv6 is enabled in the web-based manager. The fields displayed in the table depend on which IP version is selected. |
Type: | Select one of the following route types to search the routing table and display routes of the selected type only: All — all routes recorded in the routing table. Connected — all routes associated with direct connections to FortiGate unit interfaces. Static — the static routes that have been added to the routing table manually. RIP — all routes learned through RIP. For more information see “Routing Information Protocol (RIP)”. RIPNG — all routes learned through RIP version 6 (which enables the sharing of routes through IPv6 networks). BGP — all routes learned through BGP. For more information see “Border Gateway Protocol (BGP)”. OSPF — all routes learned through OSPF. For more information see “Open Shortest Path First (OSPF)”. OSPF6 — all routes learned through OSPF version 6 (which enables the sharing of routes through IPv6 networks). IS-IS — all routes learned through IS-IS. For more information see “Intermediate System to Intermediate System Protocol (IS-IS)”. HA — RIP, OSPF, and BGP routes synchronized between the primary unit and the subordinate units of a high availability (HA) cluster. HA routes are maintained on subordinate units and are visible only if you are viewing the router monitor from a virtual domain that is configured as a subordinate virtual domain in a virtual cluster. Not displayed when IP version IPv6 is selected. For details about HA routing synchronization, see the FortiGate HA User Guide. |
Network: | Enter an IP address and netmask (for example, 172.16.14.0/24) to search the routing table and display routes that match the specified network. |
Gateway: | Enter an IP address and netmask (for example, 192.168.12.1/32) to search the routing table and display routes that match the specified gateway. |
Apply Filter | Select to search the entries in the routing table based on the specified search criteria and display any matching routes. Not displayed when IP version IPv6 is selected. |
Type | The type values assigned to FortiGate unit routes (Static, Connected, RIP, OSPF, or BGP). Not displayed when IP version IPv6 is selected. |
Subtype | If applicable, the subtype classification assigned to OSPF routes. An empty string implies an intra-area route. The destination is in an area to which the FortiGate unit is connected. OSPF inter area — the destination is in the OSPF AS, but the FortiGate unit is not connected to that area. External 1 — the destination is outside the OSPF AS. This is known as OSPF E1 type. The metric of a redistributed route is calculated by adding the external cost and the OSPF cost together. External 2 — the destination is outside the OSPF AS. This is known as OSPF E2 type. In this case, the metric of the redistributed route is equivalent to the external cost only, expressed as an OSPF cost. OSPF NSSA 1 — same as External 1, but the route was received through a not-so-stubby area (NSSA). OSPF NSSA 2 — same as External 2, but the route was received through a not-so-stubby area. For more information on OSPF subtypes, see “OSPF Background and concepts”. Not displayed when IP version 6 is selected. |
Network | The IP addresses and network masks of destination networks that the FortiGate unit can reach. |
Distance | The administrative distance associated with the route. A value of 0 means the route is preferable compared to other routes to the same destination, and the FortiGate unit may routinely use the route to communicate with neighboring routers and access servers. Modifying this distance for dynamic routes is route distribution. See “Redistributing and blocking routes in BGP” Not displayed when IP version 6 is selected. |
Metric | The metric associated with the route type. The metric of a route influences how the FortiGate unit dynamically adds it to the routing table. The following are types of metrics and the protocols they are applied to. Hop count — routes learned through RIP. Relative cost — routes learned through OSPF. Multi-Exit Discriminator (MED) — routes learned through BGP. However, several attributes in addition to MED determine the best path to a destination network. For more information on BGP attributes, see “BGP attributes”. By default, the MED value associated with a BGP route is zero. However, the MED value can be modified dynamically. If the value was changed from the default, the Metric column will display a non-zero value. Not displayed when IP version 6 is selected. |
Gateway | The IP addresses of gateways to the destination networks. |
Interface | The interface through which packets are forwarded to the gateway of the destination network. |
Up Time | The total accumulated amount of time that a route learned through RIP, OSPF, or BGP has been reachable. Not displayed when IP version IPv6 is selected. |