Understanding FortiDDoS Asymmetric Mode
An asymmetric route is one in which the inbound traffic traverses the FortiDDOS system, but outbound traffic takes a route that does not.
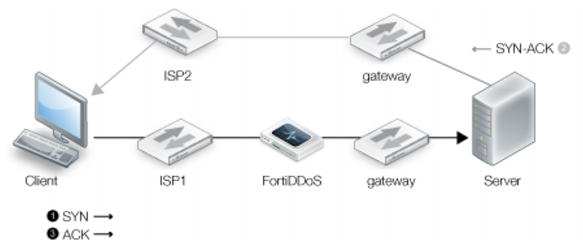
Figure 18 shows an asymmetric route when an external client initiates the connection, such as a web server request. The initial TCP SYN traverses the network path where FortiDDoS has been deployed, but the SYN-ACK response takes a different route to the client.
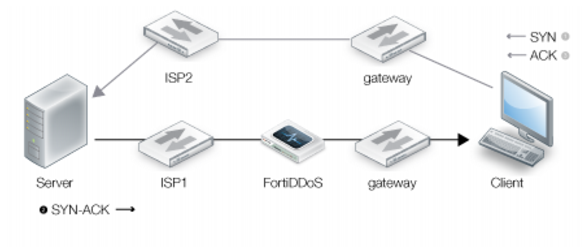
Figure 19 shows an asymmetric route when the internal resource initiates the connection, such as when a backup server initiates a scheduled job. The TCP SYN takes an out-of-path route, and the SYN-ACK packet is the first packet that FortiDDoS sees for the session.
We have two key recommendations if you plan to deploy the FortiDDOS appliance in a network path where asymmetric routes are possible:
• When feasible, design the network routes so that FortiDDoS sees both sides of the client-server connection. You might be able to do this with the preferred routes, persistence, or active/active synchronization features of the routing devices in your deployment.
• If you cannot avoid asymmetric traffic, enable FortiDDoS Asymmetric Mode. In Asymmetric Mode, FortiDDoS can use 95% of its methods to detect abnormal network traffic.
In Asymmetric Mode, the system can parse Layer 4 and Layer 7 headers for most floods and URL-related features. If this feature is off, such floods are not detected when two-way session traffic is not completely seen by the appliance.
You must enable both Asymmetric Mode and the Allow Inbound SYN-ACK option so the system can properly handle asymmetric TCP traffic. When enabled, the system treats an inbound SYN-ACK as if a SYN, and it creates an entry for it in the TCP connection table. It does not increment the syn threshold counter, but it does track syn-per-src in order to protect against attacks that might attempt to exploit this behavior.
TCP state anomaly detection depends on tracking a two-way traffic flow, so some feature options on the Protection Profiles > SPP Settings page do not work in Asymmetric Mode.
Table 7 summarizes the configuration guidelines for these feature options.
Table 10: Recommended TCP state anomaly detection settings in Asymmetric Mode
Setting | Guidelines |
syn-validation | Recommended. This option enables SYN flood mitigation mode. |
seq-validation | Do not enable. Depends on tracking a two-way traffic flow. |
state-transition-anomalies-validation | Do not enable. Depends on tracking a two-way traffic flow. |
foreign-packet-validation | Recommended. In Asymmetric Mode, FortiDDoS can still track foreign packets. |
allow-tuple-reuse | Enabled by default to support standard test environments that reuse tuples in quick succession. The setting is valid in Asymmetric Mode. Recommended to avoid unnecessary logging of the event when it is detected. |
allow-duplicate-syn-in-syn-sent | Not enabled by default, but the setting is valid in Asymmetric Mode. Recommended when FortiDDoS is in Detection Mode to avoid unnecessary logging of the event when it is detected. |
allow-duplicate-syn-in-syn-recv allow-syn-anomaly allow-syn-ack-anomaly allow-ack-anomaly allow-rst-anomaly allow-fin-anomaly | Do not enable. |
Workflow for getting started with Asymmetric Mode
1. Go to Global Settings > Settings and enable the following settings:
• Asymmetric Mode
• Allow inbound SYN/ACK
2. Get started in Detection Mode:
a. For each SPP, go to Protection Profiles > SPP Settings and ensure that the following TCP state anomaly options are enabled and no other:
• syn-validation
• foreign-packet-validation
• allow-tuple-reuse
• allow-duplicate-syn-in-syn-sent
b. Enable Detection Mode.
c. Establish a baseline of traffic statistics and set thresholds.
3. Change settings to the ones appropriate for Prevention Mode when there is asymmetric traffic:
a. For each SPP, go to Protection Profiles > SPP Settings and ensure that the following TCP state anomaly options are enabled and no other:
• syn-validation
• foreign-packet-validation
• allow-tuple-reuse
b. Enable Prevention Mode.