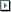
SNMP parameters are displayed on the GUI by clicking on the System configuration tab on the left navigational pane and then selecting Global to expand the branch. Click on SNMP to display the following:

The parameters are as follows:
System Name - this is the name assigned to the system.
Community String - Any SNMP management console needs to send the correct community string along with all SNMP requests. If the sent community string is not correct, FortiADC discards the request and will not respond.
System Contact - Contact is the name of the person responsible for this unit.
System Location - Location describes FortiADC’s physical location.
System Descriptions - this is the user-assigned description of FortiADC.
Click on Commit to save your changes.
 SNMP Parameters using the GUI:
SNMP Parameters using the GUI: