4. Configure these settings: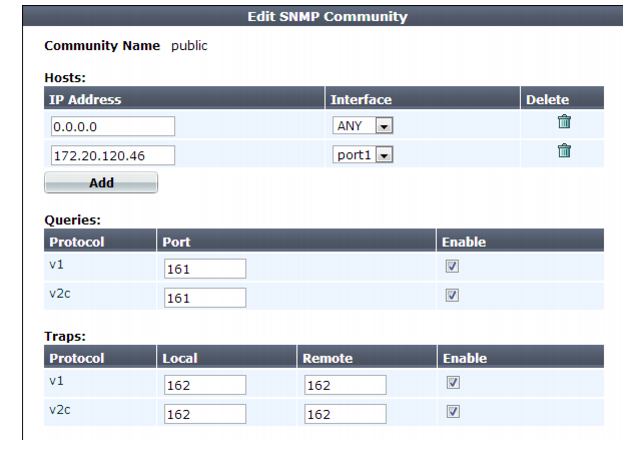


Setting name | Description | |
Community Name | Type the name of the SNMP community to which the FortiWeb appliance and at least one SNMP manager belongs, such as public. The FortiWeb appliance will not respond to SNMP managers whose query packets do not contain a matching community name. Similarly, trap packets from the FortiWeb appliance will include community name, and an SNMP manager may not accept the trap if its community name does not match. Caution: Fortinet strongly recommends that you do not add FortiWeb to the community named public. This popular default name is well-known, and attackers that gain access to your network will often try this name first. | |
Hosts | ||
IP Address | Type the IP address of the SNMP manager that, if traps or queries are enabled in this community: • will receive traps from the FortiWeb appliance • will be permitted to query the FortiWeb appliance SNMP managers have read-only access. To allow any IP address using this SNMP community name to query the FortiWeb appliance, enter 0.0.0.0. For security best practice reasons, however, this is not recommended. Caution: FortiWeb sends security-sensitive traps, which should be sent only over a trusted network, and only to administrative equipment. Note: If there are no other host IP entries, entering only 0.0.0.0 effectively disables traps because there is no specific destination for trap packets. If you do not want to disable traps, you must add at least one other entry that specifies the IP address of an SNMP manager. You can add up to 8 SNMP managers. | |
Interface | Select either ANY or the name of the network interface from which the FortiWeb appliance will send traps and reply to queries. Note: You must select a specific network interface (e.g. port1, not ANY) if the SNMP manager is not on the same subnet as the FortiWeb appliance. This can occur if the SNMP manager is on the Internet or behind a router. Note: This option only configures which network interface will send SNMP traps. To configure which network interface will receive queries, see “Configuring the network interfaces”. | |
Queries | Type the port number (161 by default) on which the FortiWeb appliance listens for SNMP queries from the SNMP managers in this community, then enable queries for either or both SNMP v1 and SNMP v2c. For supported queries, see the FortiWeb MIB file and “MIB support”. | |
Traps | Type the port number (162 by default) that will be the source (Local) port number and destination (Remote) port number for trap packets sent to SNMP managers in this community, then enable traps for either or both SNMP v1 and SNMP v2c. | |
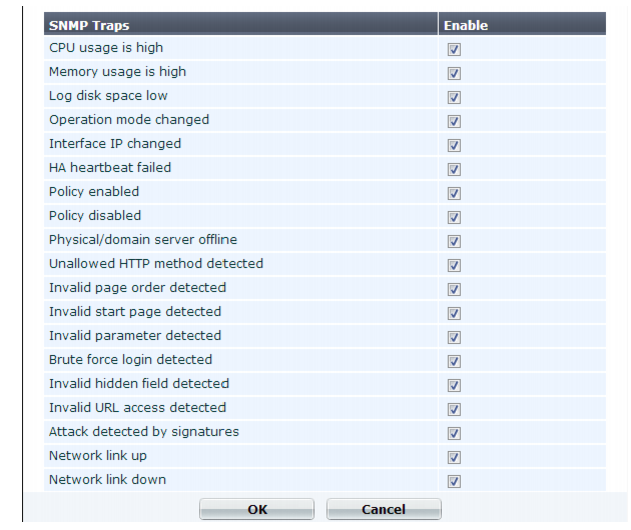 Click OK.
Click OK.While most trap events are described by their names, the following events occur when a threshold has been exceeded: • CPU usage is high — CPU usage has exceeded 80%. • Memory usage is high — Memory (RAM) usage has exceeded 80%. • Log disk space low — Disk space usage for the log partition/disk has exceeded 90%. For more information on supported traps and queries, see “MIB support”. |