Most exploits and virus exposures occur within the first 2 months of a known vulnerability. Most botnets consist of thousands of zombie computers whose IP addresses are continuously changing. To keep your defenses effective against the evolving threat landscape, Fortinet recommends FortiGuard services. New vulnerabilities and botnets are discovered and new signatures are built by Fortinet researchers every day.
Without these updates, your FortiWeb cannot detect the newest threats.
After you have subscribed to FortiGuard services, configure your FortiWeb appliance to connect to the Internet so that it can reach the world-wide Fortinet Distribution Network (FDN) in order to:
FortiWeb appliances often can connect using default settings. However, due to differences in routing and firewalling, you should confirm this by verifying connectivity.
|
|
You must first register the FortiWeb appliance with the Fortinet Technical Support web site, https://support.fortinet.com/, to receive service from the FDN. The FortiWeb appliance must also have a valid Fortinet Technical Support contract which includes service subscriptions, and be able to connect to the FDN. For port numbers required for license validation and update connections, see Appendix A: Port numbers. |
1. If your FortiWeb appliance must connect to the Internet through an explicit (non-transparent) web proxy, configure the proxy connection (see Accessing FortiGuard via a web proxy).
The appliance will attempt to validate its license when it boots. If the appliance could not connect because proxy settings were not configured, or due to any other connectivity issue that you have since resolved, you can reboot the appliance to re-attempt license validation.
2. Go to System > Status > Status.
To access this part of the web UI, your administrator's account access profile must have Read permission to items in the System Configuration category. For details, see Permissions.
3. In the FortiGuard Information widget, look at the FortiWeb Security Service row, FortiWeb Antivirus Service row, and FortiWeb IP Reputation Service row.
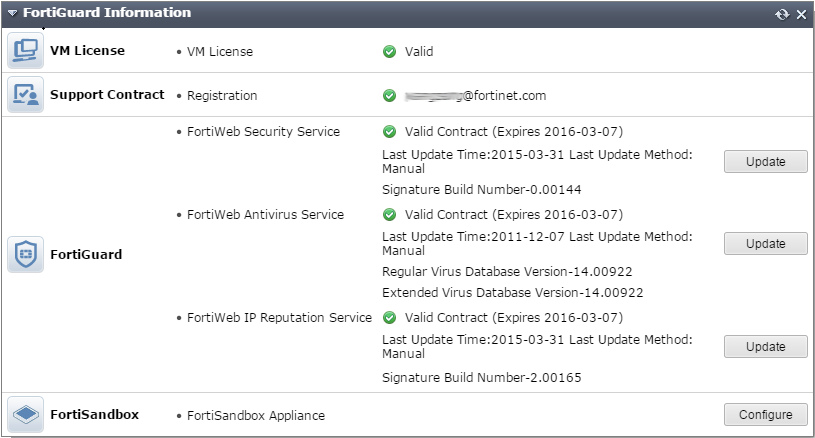
|
|
Your FortiWeb appliance cannot detect the latest vulnerabilities and compliance violations unless it is licensed and has network connectivity to download current definitions from the FortiGuard service. |
If the connection did not succeed:
nslookup to verify that FortiGuard domain names are resolving (license authentication queries are sent to update.fortiguard.net).
C:\Users\cschwartz>nslookup update.fortiguard.net
Server: google-public-dns-a.google.com
Address: 8.8.8.8
Non-authoritative answer:
Name: fds1.fortinet.com
Addresses: 209.66.81.150
209.66.81.151
208.91.112.66
Aliases: update.fortiguard.net
execute ping and execute traceroute to verify that connectivity from FortiWeb to the Internet and FortiGuard is possible. Check the configuration of any NAT or firewall devices that exist between the FortiWeb appliance and the FDN or FDS server override.
FortiWeb # exec traceroute update.fortiguard.net
traceroute to update.fortiguard.net (209.66.81.150), 32 hops max, 84 byte packets
1 192.0.2.2 0 ms 0 ms 0 ms
2 209.87.254.221 <static-209-87-254-221.storm.ca> 4 ms 2 ms 3 ms
3 209.87.239.161 <core-2-g0-3.storm.ca> 2 ms 3 ms 3 ms
4 67.69.228.161 3 ms 4 ms 3 ms
5 64.230.164.17 <core2-ottawa23_POS13-1-0.net.bell.ca> 3 ms 5 ms 3 ms
6 64.230.99.250 <tcore4-ottawa23_0-4-2-0.net.bell.ca> 16 ms 17 ms 15 ms
7 64.230.79.222 <tcore3-montreal01_pos0-14-0-0.net.bell.ca> 14 ms 14 ms 15 ms
8 64.230.187.238 <newcore2-newyork83_so6-0-0_0> 63 ms 15 ms 14 ms
9 64.230.187.42 <bxX5-newyork83_POS9-0-0.net.bell.ca> 21 ms 64.230.187.93 <BX5-NEWYORK83_POS12-0-0_core.net.bell.ca> 17 ms 16 ms
10 67.69.246.78 <Abovenet_NY.net.bell.ca> 28 ms 28 ms 28 ms
11 64.125.21.86 <xe-1-3-0.cr2.lga5.us.above.net> 29 ms 29 ms 30 ms
12 64.125.27.33 <xe-0-2-0.cr2.ord2.us.above.net> 31 ms 31 ms 33 ms
13 64.125.25.6 <xe-4-1-0.cr2.sjc2.us.above.net> 82 ms 82 ms 100 ms
14 64.125.26.202 <xe-1-1-0.er2.sjc2.us.above.net> 80 ms 79 ms 82 ms
15 209.66.64.93 <209.66.64.93.t01015-01.above.net> 80 ms 80 ms 79 ms
16 209.66.81.150 <209.66.81.150.available.above.net> 83 ms 82 ms 81 ms
1. If your FortiWeb appliance must connect to the Internet (and therefore FDN) through an explicit (non-transparent) web proxy, configure the proxy connection (see Accessing FortiGuard via a web proxy).
2. Go to System > Config > FortiGuard.
To access this part of the web UI, your administrator's account access profile must have Read and Write permission to items in the Maintenance category. For details, see Permissions.
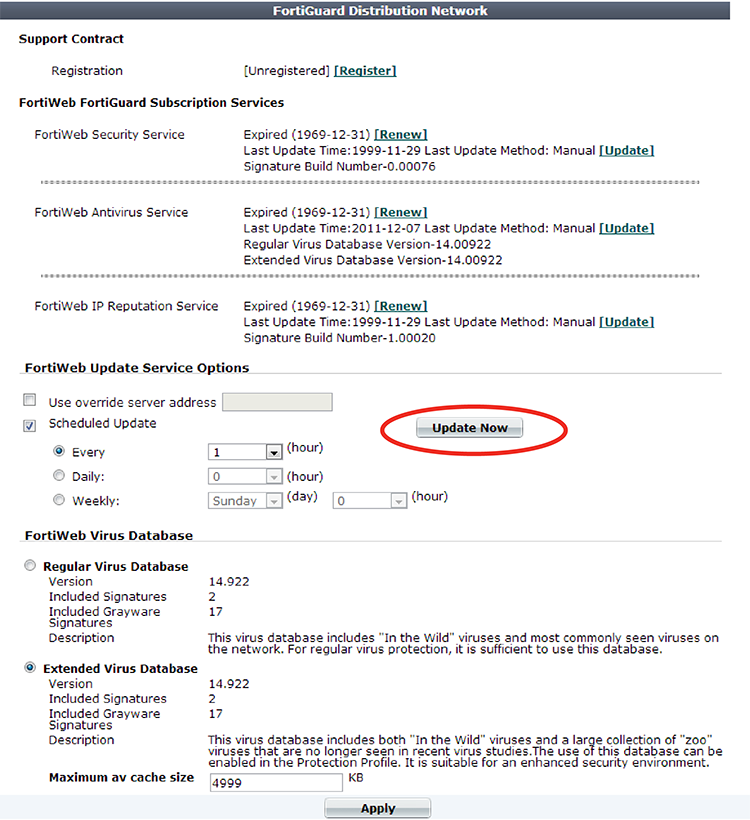
3. If you want your FortiWeb appliance to connect to a specific FDS other than the default for its time zone, enable Use override server address, and enter the IP address and port number of an FDS in the format <FDS_ipv4>:<port_int>, such as 10.0.0.1:443.
4. Click Apply.
5. Click Update Now.
The FortiWeb appliance tests the connection to the FDN and, if any, the server you specified to override the default FDN server. Time required varies by the speed of the FortiWeb appliance’s network connection, and by the number of timeouts that occur before the connection attempt is successful or the FortiWeb appliance determines that it cannot connect. If you have enabled logging in:
test results are indicated in Log & Report > Log Access > Event
If the connection test did not succeed due to license issues, you would instead see this log message:
For more troubleshooting information, enter the following commands:
diagnose debug enable
diagnose debug application fds 8
These commands display cause additional information in your CLI console. For example:
FortiWeb # [update]: Poll timeout.
FortiWeb # *ATTENTION*: license registration status changed to 'VALID',please logout and re-login
For example, poll (license and update request) timeouts can be caused by incorrectly configured static routes and DNS settings, links with high packet loss, and other basic connectivity issues. Unless you override the behavior with a specific FDS address (enable and configure Use override server address), FortiWeb appliances connect to the FDN by connecting to the server nearest to the FortiWeb appliance by its configured time zone. Timeouts can therefore also be caused by incorrect time zone.
Most viruses are actively spreading initially, but as hosts are patched and more networks filter them out, their occurrence becomes more rare.
Fortinet’s FortiGuard Global Security Research Team continuously monitor detections of new and older viruses. When a specific virus has not been detected for one year, it is considered to be dormant. It is possible that a new outbreak could revive it, but that is increasingly unlikely as time passes due to replacement of vulnerable hardware and patching of vulnerable software. Therefore dormant viruses’s signatures are removed from the “Regular” database, but preserved in the “Extended” signature database.
If your FortiWeb’s performance is more critical than the risk of these dormant viruses, you can choose to omit signatures for obsolete viruses by selecting the “Regular” database on System > Config > FortiGuard.

| Setting name | Description |
|---|---|
| Regular Virus Database | Select to use only the signatures of viruses and greyware that have been detected by FortiGuard’s networks to be recently spreading in the wild. |
| Extended Virus Database | Select to use all signatures, regardless of whether the viruses or greyware are currently spreading. |
| Maximum Antivirus Buffer Size | Type the maximum size in kilobytes (KB) of the memory buffer that FortiWeb uses to temporarily undo the compression that a client or web server has applied to traffic, in order to inspect and/or modify it. See Configuring temporary decompression for scanning & rewriting. Caution: Unless you configure otherwise, compressed requests that are too large for this buffer pass through FortiWeb without scanning or rewriting. This could allow viruses to reach your web servers, and cause HTTP body rewriting to fail. If you prefer to block requests greater than this buffer size, configure Body Length. To be sure that it will not disrupt normal traffic, first configure Action to be Alert. If no problems occur, switch it to Alert & Deny. |
Using the CLI, you can configure the FortiWeb appliance to connect through an explicit (non-transparent) web proxy server to the FortiGuard Distribution Network (FDN) for signature updates.
For example, you might enter the following commands:
config system autoupdate tunneling
set status enable
set address 192.168.1.10
set port 8080
set username FortiWeb
set password myPassword1
end
For details, see the FortiWeb CLI Reference.
The FortiWeb appliance connects to the proxy using the HTTP CONNECT method, as described in RFC 2616.
Security is only as good as your most recent update. Without up-to-date signatures and blacklists, your network would be vulnerable to new attacks. However, if the updates were released before adequate testing and not accurate, FortiWeb scans would result in false positives or false negatives. For maximum benefit and minimum risk, updates must balance the two needs: to be both accurate and current.
Fortinet releases FortiGuard updates according to the best frequency for each technology.
Your FortiWeb appliance uses signatures, IP lists, and data type definitions for many features, including to detect attacks such as:
FortiWeb also can use virus definitions to block trojan uploads, and can use IP reputation definitions to allow search engines but block botnets and anonymizing proxies preferred by hackers. FortiGuard services ensure that your FortiWeb is using the most advanced attack protections. Timely updates are crucial to defending your network.
You can configure the FortiWeb appliance to periodically poll for FortiGuard service updates from the FDN, and automatically download and apply updates if they exist.
For example, you might schedule update requests every night at 2 AM local time, when traffic volume is light.
|
|
Alternatively, you can manually upload update packages, or initiate an update request. For details, see Manually initiating update requests and Uploading signature & geography-to-IP updates. You can manually initiate updates as alternatives or in conjunction with scheduled updates. For additional/alternative update methods, see Manually initiating update requests. |
1. Verify that the FortiWeb appliance has a valid license and can connect to the FDN, or (if destination NAT is used, for example) the IP address that you are using to override the default IPs for FDN servers. For details, see To determine your FortiGuard license status and To verify FortiGuard update connectivity.
2. Go to System > Config > FortiGuard.
To access this part of the web UI, your administrator's account access profile must have Read and Write permission to items in the Maintenance category. For details, see Permissions.
The page informs you if you are not registered or if registration has expired. If your registration is active, continue scheduling updates; otherwise, click Register or Renew.
3. Enable Scheduled Update.
4. Select one of the following options:
If you select 00 minutes, the update request occurs at a randomly determined time within the selected hour.
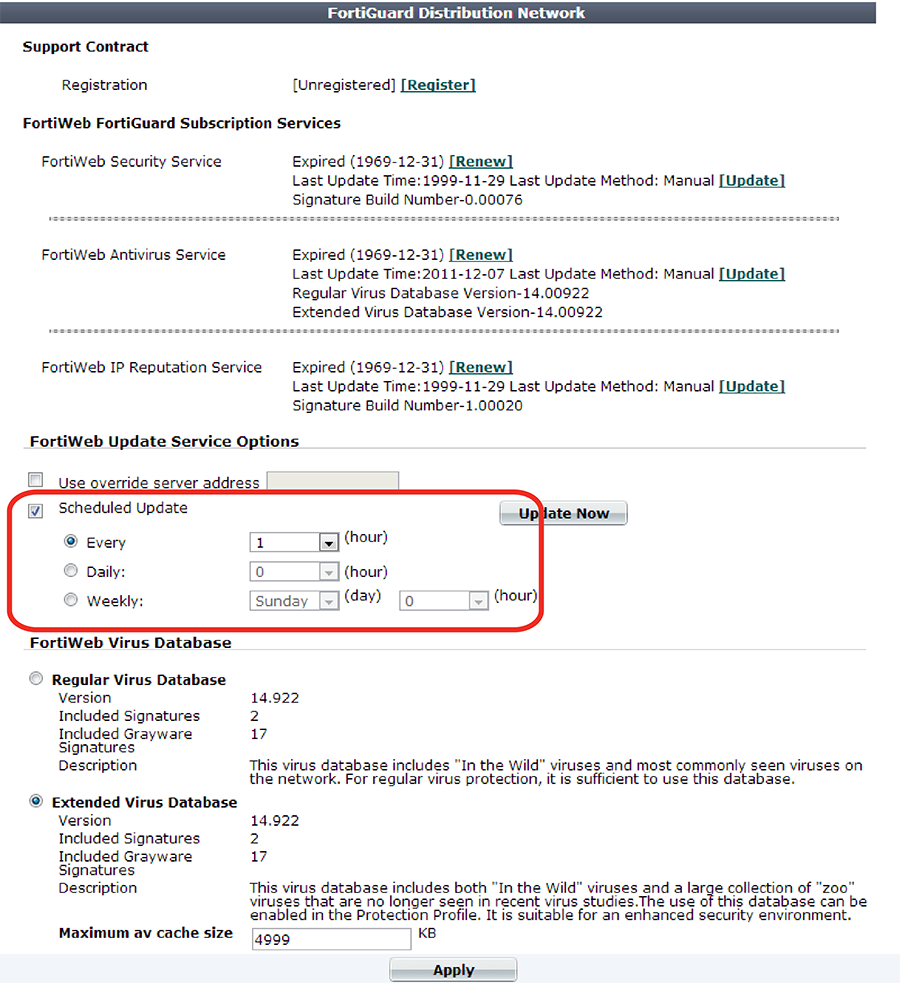
5. Click Apply.
The FortiWeb appliance next requests an update according to the schedule.
At the scheduled time, FortiWeb starts the update. Under Current update status, the following information is displayed:
This option is useful if, for example, the download is slow and you want to stop it and try again later. It can also be useful if you want to stop the scheduled update and instead update your anti-virus package using a file you have manually downloaded from the Fortinet Technical Support web site (Uploading signature & geography-to-IP updates.)

Results of the update activity appear in FortiWeb Security Service in the FortiGuard Information widget. If you have enabled logging in:
when the FortiWeb appliance requests an update, the event is recorded in Log & Report > Log Access > Event, such as these log message:
FortiWeb virus signature is already up-to-date
FortiWeb IP reputation signature update succeeded
If the FortiWeb appliance cannot successfully connect, it records a log with a message that varies by the cause of the error, such as:
FortiWeb is unauthorized.
Once the attack signature update is complete, FortiWeb immediately begins to use them. No reboot is required.
If an important update has been released but there is too much time remaining until your appliance’s next scheduled update poll, you can manually trigger the FortiWeb appliance to connect to the FDN or FDS server override to request available updates for its FortiGuard service packages.
|
|
You can manually initiate updates as an alternative or in addition to other update methods. For details, see Scheduling automatic signature updates and Uploading signature & geography-to-IP updates. |
1. Before manually initiating an update, first verify that the FortiWeb appliance has a valid license and can connect to the FDN or override server. For details, see To determine your FortiGuard license status and To verify FortiGuard update connectivity.
2. Go to System > Config > FortiGuard.
To access this part of the web UI, your administrator's account access profile must have Read and Write permission to items in the Maintenance category. For details, see Permissions.

3. Click Update Now.
The web UI displays a message similar to the following:
Your update request has been sent. Your database will be updated in a few minutes. Please check your update page for the status of the update.
After the update starts, under Current update status, the following information is displayed:
The name of the update package that is currently downloading, the start time of the download operation, and the percentage complete.
A Refresh button, which allows you to update the package download status information.
If FortiWeb is downloading an anti-virus package, a Stop button.
This option is useful if, for example, the download is slow and you want to stop it and try again later. It can also be useful if you want to stop the scheduled update and instead update your anti-virus package using a file you have manually downloaded from the Fortinet Technical Support web site (Uploading signature & geography-to-IP updates.)

Results of the update activity appear in FortiWeb Security Service in the FortiGuard Information widget. If you have enabled logging in:
when the FortiWeb appliance requests an update, the event is recorded in Log & Report > Log Access > Event, such as these log message:
FortiWeb virus signature is already up-to-date
FortiWeb IP reputation signature update succeeded
If the FortiWeb appliance cannot successfully connect, it will record a log with a message that varies by the cause of the error, such as:
Once the attack signature update is complete, FortiWeb will immediately begin to use them. No reboot is required.
You can manually update the geography-to-IP mappings and the attack, virus, and botnet signatures that your FortiWeb appliance uses to detect attacks. Updating these ensures that your FortiWeb appliance can detect recently discovered variations of these attacks, and that it knows about the current statuses of all IP addresses on the public Internet.
After restoring the firmware of the FortiWeb appliance, you should install the most currently available packages through FortiGuard. Restoring firmware installs the packages that were current at the time the firmware image file was made: they may no longer be up-to-date.
|
|
Alternatively, you can schedule automatic updates, or manually trigger the appliance to immediately request an update. For details, see Scheduling automatic signature updates and Manually initiating update requests. This does not, however, update geography-to-IP mappings, which still must be uploaded manually. |
1. Download the file from the Fortinet Technical Support web site:
2. Log in to the web UI of the FortiWeb appliance as the admin administrator, or an administrator account whose access profile contains Read and Write permissions in the Maintenance category.
3. Go to System > Config > FortiGuard.
4. In the row next to the service whose signatures you want to upload, click the Update link.
A dialog appears that allows you to upload the file.
5. Click the Browse button (its name varies by browser) and select the signatures file, then click OK.
Your browser uploads the file. Time required varies by the size of the file and the speed of your network connection. Once the attack signature update is complete, FortiWeb will immediately begin to use them. No reboot is required.