Administrator access
• As soon as possible during initial FortiRecorder setup, give the default administrator, admin, a password. This super-administrator account has the highest level of permissions possible, and access to it should be limited to as few people as possible.
• Administrator passwords should be at least 8 characters long and include both numbers and letters.
• Change all passwords regularly. Set a policy — such as every 60 days — and follow it.
• Instead of allowing administrative access to the FortiRecorder appliance from any source, restrict it to trusted internal hosts. On those computers that you have designated for management, apply strict patch and security policies. Always password-encrypt any FortiRecorder configuration backup that you download to those computers to mitigate the information that attackers can gain from any potential compromise. If your computer’s operating system does not support this, you can use third-party software to encrypt the file.
• Do not give administrator-level access to all people who use the system. Usually, only a network administrator should have access to the network settings. Others should have operator accounts. This prevents others from accidentally or maliciously breaking the appliance’s connections with cameras and computers. See
“User management”.
• By default, an administrator login that is idle for more than five minutes times out. You can change this to a longer period in the idle timeout settings. But Fortinet does not recommend it. Left unattended, a web UI or CLI session could allow anyone with physical access to your computer to change FortiRecorder settings. Small idle timeouts mitigate this risk.
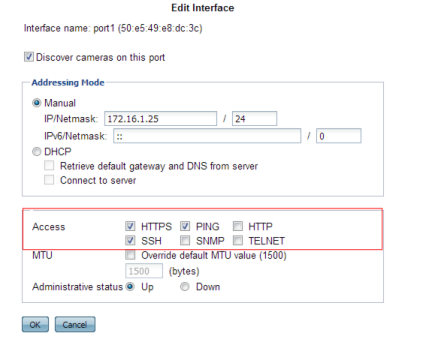
• Restrict administrative access to a single network interface (usually port1), and allow only the management access protocols needed.
Use only the most secure protocols. Disable
PING, except during troubleshooting. Disable
HTTP,
SNMP, and
TELNET unless the network interface only connects to a trusted, private administrative network. See
“NVR configuration”.
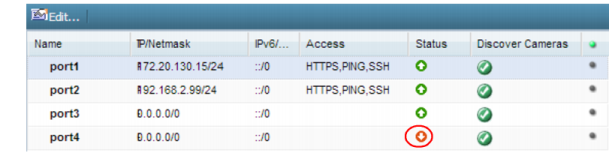
• Disable all network interfaces that should not receive any traffic. (i.e. Set the
Administrative status to
Down.)
For example, if administrative access is typically through port1, the Internet is connected to port2, and cameras are connected to port3, you would disable (“bring down”) port4. This would prevent an attacker with physical access from connecting a cable to port4 and thereby gaining access if the configuration inadvertently allows it.