IPsec VPN
This chapter describes new IPsec VPN features added to FortiOS 5.4.
Added warning message in IPsec VPN wizard if users selects ANY for peer ID (357043)
If users change the peertype setting back to any, either via CLI or GUI, they receive a warning that clearly informs them that using a setting of any will allow remote connections generated by any CA trusted by this FortiGate to be established.
- Warning icon shows up in IPsec tunnel page when setting peertype to any in VPN tunnel.
- Warning message shows up in IPsec tunnel editing page when setting peertype to any in VPN tunnel.
- In the VPN wizard configuration page, option peer certificate CA is added which is used to create the related peer user through VPN wizard.
- Peertype is set to peer certificate by default in GUI when setting authmethod to signature for custom IPsec tunnel.
IKEv1 Quick Crash Detection (304612)
Based on the IKEv2 quick crash detection (QCD) feature in Mantis 298970, which is already in the new features list for FortiOS 5.4 below.
There is no RFC for this feature. It is implemented using a new IKE vendor ID, "Fortinet Quick Crash Detection", and so both endpoints must be FortiGate devices. The QCD token is sent in the Phase 1 exchange and must be encrypted, so this is only implemented for IKEv1 in Main mode (Aggressive mode is not supported as there is no available AUTH message in which to include the token).
Otherwise, the feature works the same as in IKEv2 (RFC 6290).
IKE mode-cfg IPv4/IPv6 dual stack support (303550)
The previous IKE CLI uses the mode-cfg-ip-version option to specify whether mode-cfg should assign an IPv4 or IPv6 address, but this is not ideal for customers that require dual stack support.
As a solution in FortiOS 5.4.1, the phase1 mode-cfg-ip-version option was removed. The option was not necessary because the IP version can be determined by the selector type (dst-addr-type) of the configured Phase 2 tunnel(s). If the FortiGate client config contains Phase 2 tunnels for both IPv4 and IPv6, then the FortiGate client will request IPv4 and IPv6 addresses during mode-cfg.
Additionally, the FGT server can now be configured to reply with either or both IPv4 and IPv6, as per the client's mode-cfg request.
Security improvements to the default IPsec VPN signature and peer type configuration (304894 307500 307490 355149)
New features have been introduced to make certification and implementation in IPsec VPN more secure by default. Users can now create PKI certificates in-line in the VPN editor.
In short:
- Reimplemented PKI dialogs such that changes to enforce attributes are done in new frameworks
- Changed default templates for VPN wizard to enforce
peertype=anyso that wizard tunnels can be created - Will now default to PKI string when creating signature VPN via VPN edit
Remote IP address change detection (209553)
This feature changes the way IPsec SAs are tracked in the kernel in order to detect external IP address changes in the tunnel.
Previously, SAs were stored when keyed off of the remote IP address. Now, SAs are stored in a hash table when keyed off the IPsec SA SPI value (which is actually more RFC compliant). This enables the FortiGate, for each inbound ESP packet received, to immediately look up the SA and compare the stored IP address against the one in the incoming packet. If the incoming and stored IP addresses differ, an IP address change can be made in the kernel SA, and an update event can be triggered for IKE.
IKE/IPsec Extended Sequence Number (ESN) support (255144)
This feature implements negotiation of 64-bit Extended Sequence numbers as described in RFC 4303, RFC 4304 as an addition to IKEv1, and RFC 5996 for IKEv2.
Updates and enhancements to the IPsec VPN wizard (222339 290377 287021 289251)
The IPsec VPN wizard has been simplified to more clearly identify tunnel template types, remote device types, and NAT configuration requirements. Example topological diagrams are now also included.
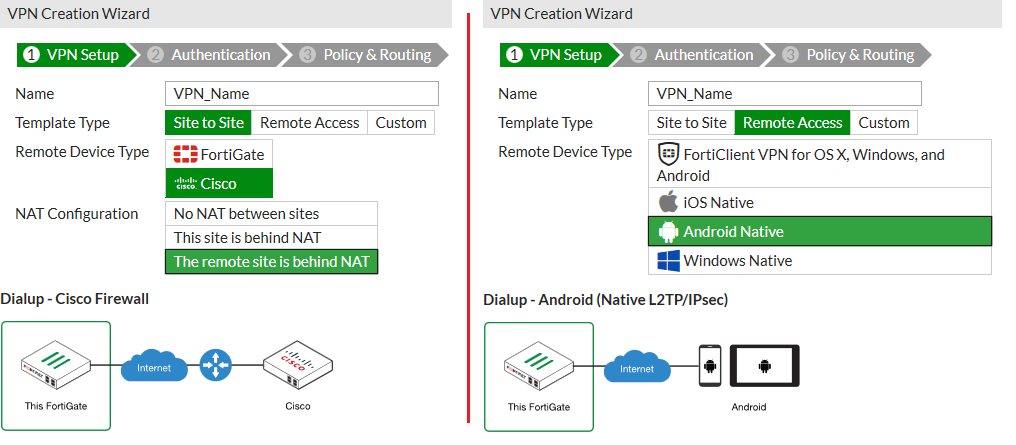
New Dialup - FortiGate and Dialup - Windows (Native L2TP/IPsec) tunnel template options.
Cisco compatible keep-alive support for GRE (261595)
The FortiGate can now send a GRE keep-alive response to a Cisco device to detect a GRE tunnel. If it fails, it will remove any routes over the GRE interface.
Syntax
config system gre-tunnel
edit <id>
set keepalive-interval <value: 0-32767>
set keepalive-failtimes <value: 1-255>
next
end
Repeated Authentication in Internet Key Exchange (IKEv2) Protocol (282025)
This feature provides the option to control whether a device requires its peer to re-authenticate or whether re-key is sufficient. It does not influence the re-authentication or re-key behavior of the device itself, which is controlled by the peer (with the default being to re-key).
This solution is in response to RFC 4478. As described by the IETF, "the purpose of this is to limit the time that security associations (SAs) can be used by a third party who has gained control of the IPsec peer".
Syntax
config vpn ipsec phase1-interface
edit p1
set reauth [enable | disable]
next
end
Improvements to IPsec VPN in ADVPN hub-and-spoke (275322)
IPsec VPN traffic is now allowed through a tunnel between an ADVPN hub-and-spoke
config vpn ipsec phase1-interface
edit "int-fgtb"
...
set auto-discovery-sender [enable | disable]
set auto-discovery-receiver [enable | disable]
set auto-discovery-forwarder [enable | disable]
...
next
end
config vpn ipsec phase2-interface
edit "int-fgtb"
...
set auto-discovery-sender phase1 [enable | disable]
...
next
end
ADVPN support for NAT device (299798)
The ADVPN feature has been extended so that it allows ADVPN shortcuts to be negotiated as long as one of the devices is not behind NAT.
The on-the-wire format of the ADVPN messages was changed so that they use TLV encoding. Since the on-the-wire format has changed this is not compatible with any previous ADVPN builds.
AES-GCM support (281822)
AES-GCM (128 | 256) AEAD has been added, as specified in RFC 4106:
config vpn ipsec phase1-interface
edit "tofgta"
...
set suite-b disable | suite-b-gcm-128 | suite-b-gcm-256
...
next
end
config vpn ipsec phase2-interface
edit "tofgta"
set phase1name "tofgta"
set proposal aes128gcm aes256gcm
...
next
end
IPsec tunnel idle timer (244180)
Add a command to define an idle timer for IPsec tunnels when no traffic has passed through the tunnel for the configured idle-timeout value, the IPsec tunnel will be flushed.
config vpn ipsec phase1-interface
edit p1
set idle-timeout enable/disable
set idle-timeoutinterval <integer> //IPsec tunnel idle timeout in minutes (10 - 43200).
end
end
SAs negotiation improvement (245872)
The IPsec SA connect message generated is used to install dynamic selectors. These selectors can now be installed via the auto-negotiate mechanism. When phase 2 has auto-negotiate enabled, and phase 1 has mesh-selector-type set to subnet, a new dynamic selector will be installed for each combination of source and destination subnets. Each dynamic selector will inherit the auto-negotiate option from the template selector and begin SA negotiation. Phase 2 selector sources from dial-up clients will all establish SAs without traffic being initiated from the client subnets to the hub.
Add VXLAN over IPsec (265556)
Packets with VXLAN header are encapsulated within IPsec tunnel mode. New attributes in IPsec phase1 settings have been added.
config vpn ipsec phase1-interface/phase1
edit ipsec
set interface <name>
set encapsulation vxlan/gre (new)
set encapsulation-address ike/ipv4/ipv6 (New)
set encap-local-gw4 xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx (New)
set encap-remote-gw xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx (New)
next
end
Ability to enable/disable IPsec ASIC-offloading (269555)
Much like NPU-offload in IKE phase1 configuration, this feature enables/disables the usage of ASIC hardware for IPsec Diffie-Hellman key exchange and IPsec ESP traffic. Currently by default hardware offloading is used. For debugging purposes, sometimes we want all the traffic to be processed by software.
config sys global
set ipsec-asic-offload [enable | disable]
end
Added an option to force IPsec to use NAT Traversal (275010)
Added a new option for NAT. If NAT is set to Forced, then the FGT will use a port value of zero when constructing the NAT discovery hash for the peer. This causes the peer to think it is behind a NAT device, and it will use UDP encapsulation for IPsec, even if no NAT is present. This approach maintains interoperability with any IPsec implementation that supports the NAT-T RFC.
Add a feature to support IKEv2 Session Resumption described in RFC 5723 (289914)
If a gateway loses connectivity to the network, clients can attempt to re-establish the lost session by presenting the ticket to the gateway. As a result, sessions can be resumed much faster, as DH exchange that is necessary to establish a brand new connection is skipped. This feature implements "ticket-by-value", whereby all information necessary to restore the state of a particular IKE SA is stored in the ticket and sent to the client.
Added support for IKEv2 Quick Crash Detection (298970)
A new feature has been added to support IKEv2 Quick Crash Detection as described in RFC 6290.
RFC 6290 describes a method in which an IKE peer can quickly detect that the gateway peer that it has and established IKE session with, has rebooted, crashed, or otherwise lost IKE state. When the gateway receives IKE messages or ESP packets with unknown IKE or IPsec SPIs, the IKEv2 protocol allows the gateway to send the peer an unprotected IKE message containing INVALID_IKE_SPI or INVALID_SPI notification payloads.
RFC 6290 introduces the concept of a QCD token, which is generated from the IKE SPIs and a private QCD secret, and exchanged between peers during the protected IKE AUTH exchange.
CLI Syntax
config system settings
set ike-quick-crash-detect [enable | disable]
end
- If updating to FortiOS 5.4.1, see above (304612).
Removed support for auto-IPsec (300893)
IPsec auto-VPN support (auto-IPsec) has been removed. This feature was added in FortiOS 5.0 prior to any usable VPN creation support on the GUI. As of 5.2, and now in 5.4, the wizard solves many of the problems introduced by the auto-IPsec feature, and so auto-IPsec has been deprecated.
Improved scalability for IPsec DPD (292500)
On a dial-up server, if a multitude of VPN connections are idle, the increased DPD exchange could negatively impact the performance/load of the daemon. For this reason, an option has been added to send DPD passively in a mode called "on-demand".
config vpn ipsec phase1-interface
edit <value>
set dpd [disable | on-idle | on-demand]
next
end
Notes
- When there is no traffic and the last DPD-ACK had been received, IKE will not send DPDs periodically.
- IKE will only send out DPDs if there are outgoing packets to send but no inbound packets had since been received.
Syntax
The set dpd enable command has changed to set dpd on-idle (to trigger DPD when IPsec is idle). Set DPD to on-demand to trigger DPD when IPsec traffic is sent but no reply is received from the peer.
configure vpn ipsec phase1-interface
edit <value>
set dpd [on-idle|on-demand]
next
end

