Remote link failover
Remote link failover (also called remote IP monitoring) is similar to HA port monitoring and link health monitoring (also known as dead gateway detection). Port monitoring causes a cluster to failover if a monitored primary unit interface fails or is disconnected. Remote IP monitoring uses link health monitors configured for FortiGate interfaces on the primary unit to test connectivity with IP addresses of network devices. Usually these would be IP addresses of network devices not directly connected to the cluster. For example, a downstream router. Remote IP monitoring causes a failover if one or more of these remote IP addresses does not respond to link health checking.
By being able to detect failures in network equipment not directly connected to the cluster, remote IP monitoring can be useful in a number of ways depending on your network configuration. For example, in a full mesh HA configuration, with remote IP monitoring, the cluster can detect failures in network equipment that is not directly connected to the cluster but that would interrupt traffic processed by the cluster if the equipment failed.
Example HA remote IP monitoring topology
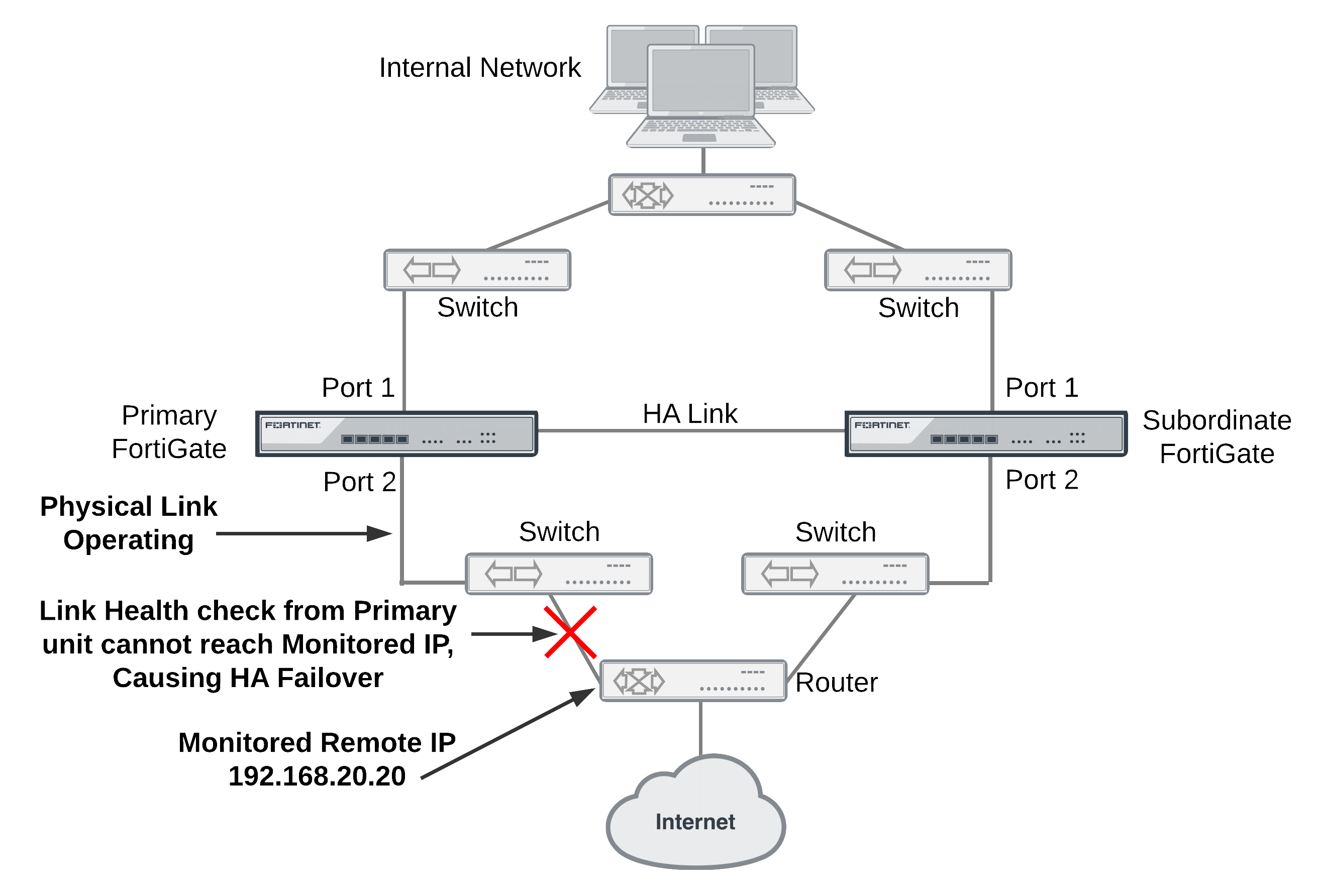
In the simplified example topology shown above, the switch connected directly to the primary unit is operating normally but the link on the other side of the switches fails. As a result traffic can no longer flow between the primary unit and the Internet.
To detect this failure you can create a link health monitor for port2 that causes the primary unit to test connectivity to 192.168.20.20. If the health monitor cannot connect to 192.268.20.20 the cluster to fails over and the subordinate unit becomes the new primary unit. After the failover, the health check monitor on the new primary unit can connect to 192.168.20.20 so the failover maintains connectivity between the internal network and the Internet through the cluster.
To configure remote IP monitoring
- Enter the following commands to configure HA remote monitoring for the example topology.
- Enter the
pingserver-monitor-interfacekeyword to enable HA remote IP monitoring on port2. - Leave the
pingserver-failover-thresholdset to the default value of 5. This means a failover occurs if the link health monitor doesn’t get a response after 5 attempts. - Enter the
pingserver-flip-timeoutkeyword to set the flip timeout to 120 minutes. After a failover, if HA remote IP monitoring on the new primary unit also causes a failover, the flip timeout prevents the failover from occurring until the timer runs out. Setting thepingserver‑flip‑timeoutto 120 means that remote IP monitoring can only cause a failover every 120 minutes. This flip timeout is required to prevent repeating failovers if remote IP monitoring causes a failover from all cluster units because none of the cluster units can connect to the monitored IP addresses.
config system ha
set pingserver-monitor-interface port2
set pingserver-failover-threshold 5
set pingserver-flip-timeout 120
end
- Enter the following commands to add a link health monitor for the port2 interface and to set HA remote IP monitoring priority for this link health monitor.
- Enter the
detectserverkeyword to set the health monitor server IP address to 192.168.20.20. - Leave the
ha-prioritykeyword set to the default value of 1. You only need to change this priority if you change the HApingserver-failover-threshold. Theha-prioritysetting is not synchronized among cluster units.
|
|
The ha-priority setting is not synchronized among cluster units. So if you want to change the ha-priority setting you must change it separately on each cluster unit. Otherwise it will remain set to the default value of 1. |
- Use the
intervalkeyword to set the time between link health checks and use thefailtimekeyword to set the number of times that a health check can fail before a failure is detected (the failover threshold). The following example reduces the failover threshold to 2 but keeps the health check interval at the default value of 5.
config system link-monitor
edit ha-link-monitor
set server 192.168.20.20
set srcintf port2
set ha-priority 1
set interval 5
set failtime 2
end
Adding HA remote IP monitoring to multiple interfaces
You can enable HA remote IP monitoring on multiple interfaces by adding more interface names to the pingserver-monitor-interface keyword. If your FortiGate configuration includes VLAN interfaces, aggregate interfaces and other interface types, you can add the names of these interfaces to the pingserver-monitor-interface keyword to configure HA remote IP monitoring for these interfaces.
For example, enable remote IP monitoring for interfaces named port2, port20, and vlan_234:
config system ha
set pingserver-monitor-interface port2 port20 vlan_234
set pingserver-failover-threshold 10
set pingserver-flip-timeout 120
end
Then configure health monitors for each of these interfaces. In the following example, default values are accepted for all settings other than the server IP address.
config system link-monitor
edit port2
set server 192.168.20.20
next
edit port20
set server 192.168.20.30
next
edit vlan_234
set server 172.20.12.10
end
Changing the link monitor failover threshold
If you have multiple link monitors you may want a failover to occur only if more than one of them fails.
For example, you may have 3 link monitors configured on three interfaces but only want a failover to occur if two of the link monitors fail. To do this you must set the HA priorities of the link monitors and the HA pingserver-failover-threshold so that the priority of one link monitor is less than the failover threshold but the added priorities of two link monitors is equal to or greater than the failover threshold. Failover occurs when the HA priority of all failed link monitors reaches or exceeds the threshold.
For example, set the failover threshold to 10 and monitor three interfaces:
config system ha
set pingserver-monitor-interface port2 port20 vlan_234
set pingserver-failover-threshold 10
set pingserver-flip-timeout 120
end
Then set the HA priority of link monitor server to 5.
|
|
The HA Priority (ha-priority) setting is not synchronized among cluster units. In the following example, you must set the HA priority to 5 by logging into each cluster unit. |
config system link-monitor
edit port2
set srcintf port2
set server 192.168.20.20
set ha-priority 5
next
edit port20
set srcintf port20
set server 192.168.20.30
set ha-priority 5
next
edit vlan_234
set srcintf vlan_234
set server 172.20.12.10
set ha-priority 5
end
If only one of the link monitors fails, the total link monitor HA priority will be 5, which is lower than the failover threshold so a failover will not occur. If a second link monitor fails, the total link monitor HA priority of 10 will equal the failover threshold, causing a failover.
By adding multiple link monitors and setting the HA priorities for each, you can fine tune remote IP monitoring. For example, if it is more important to maintain connections to some networks you can set the HA priorities higher for these link monitors. And if it is less important to maintain connections to other networks you can set the HA priorities lower for these link monitors. You can also adjust the failover threshold so that if the cluster cannot connect to one or two high priority IP addresses a failover occurs. But a failover will not occur if the cluster cannot connect to one or two low priority IP addresses.
Monitoring multiple IP addresses from one interface
You can add multiple IP addresses to a single link monitor to use HA remote IP monitoring to monitor more than one IP address from a single interface. If you add multiple IP addresses, the health checking will be with all of the addresses at the same time. The link monitor only fails when no responses are received from all of the addresses.
config system link-monitor
edit port2
set srcintf port2
set server 192.168.20.20 192.168.20.30 172.20.12.10
end
Flip timeout
The HA remote IP monitoring configuration also involves setting a flip timeout. The flip timeout is required to reduce the frequency of failovers if, after a failover, HA remote IP monitoring on the new primary unit also causes a failover. This can happen if the new primary unit cannot connect to one or more of the monitored remote IP addresses. The result could be that until you fix the network problem that blocks connections to the remote IP addresses, the cluster will experience repeated failovers. You can control how often the failovers occur by setting the flip timeout. The flip timeout stops HA remote IP monitoring from causing a failover until the primary unit has been operating for the duration of the flip timeout.
If you set the flip timeout to a relatively high number of minutes you can find and repair the network problem that prevented the cluster from connecting to the remote IP address without the cluster experiencing very many failovers. Even if it takes a while to detect the problem, repeated failovers at relatively long time intervals do not usually disrupt network traffic.
Use the following command to set the flip timeout to 3 hours (360 minutes):
config system ha
set pingserver-flip-timeout 360
end
Restoring normal cluster operation after the remote link is restored
In a remote IP monitoring configuration, if you also want the same cluster unit to always be the primary unit you can set its device priority higher and enable override. With this configuration, when a remote IP monitoring failover occurs, after the flip timeout expires another failover will occur (because override is enabled) and the unit with override enabled becomes the primary unit again. So the cluster automatically returns to normal operation.
The primary unit starts remote IP monitoring again. If the remote link is restored the cluster continues to operate normally. If, however, the remote link is still down, remote link failover causes the cluster to failover again. This will repeat each time the flip timeout expires until the failed remote link is restored.
You can use the pingserver-slave-force-reset option to control this behavior. By default this option is enabled and the behavior described above occurs. The overall behavior is that when the remote link is restored the cluster automatically returns to normal operation after the flip timeout.
If you disable pingserver-slave-force-reset after the initial remote IP monitoring failover nothing will happen after the flip timeout (as long as the new primary unit doesn't experience some kind of failover. The result is that repeated failovers no longer happen. But it also means that the original primary unit will remain the subordinate unit and will not resume operating as the primary unit.
Detecting HA remote IP monitoring failovers
Just as with any HA failover, you can detect HA remote IP monitoring failovers by using SNMP to monitor for HA traps. You can also use alert email to receive notifications of HA status changes and monitor log messages for HA failover log messages. In addition, FortiGates send the critical log message Ping Server is down when a ping server fails. The log message includes the name of the interface that the ping server has been added to.

