Overview of WiFi controller configuration
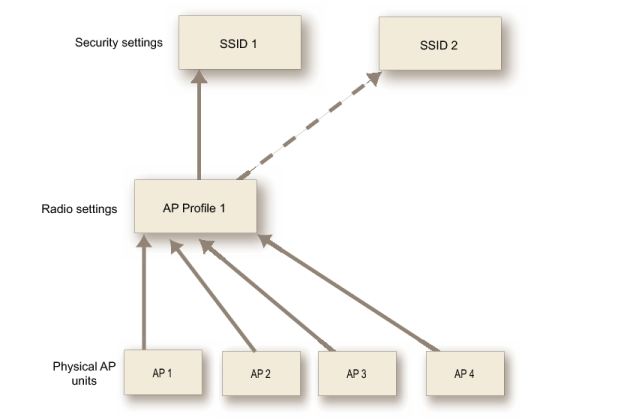
The FortiGate WiFi controller configuration is composed of three types of object, the SSID, the AP Profile and the physical Access Point.
• An SSID defines a virtual wireless network interface, including security settings. One SSID is sufficient for a wireless network, regardless how many physical access points are provided. You might, however, want to create multiple SSIDs to provide different services or privileges to different groups of users. Each SSID has separate firewall policies and authentication. Each radio in an access point can support up to 8 SSIDs.
A more common use of the term SSID is for the identifier that clients must use to connect to the wireless network. Each SSID (wireless interface) that you configure will have an SSID field for this identifier. In Managed Access Point configurations you choose wireless networks by SSID values. In firewall policies you choose wireless interfaces by their SSID name.
• An AP Profile defines the radio settings, such as band (802.11g for example) and channel selection. The AP Profile names the SSIDs to which it applies. Managed APs can use automatic profile settings or you can create custom AP profiles.
• Managed Access Points represent local wireless APs on FortiWiFi units and FortiAP units that the FortiGate unit has discovered. There is one managed access point definition for each AP device. An access point definition can use automatic AP profile settings or select a custom AP Profile. When automatic profile settings are used, the managed AP definition also selects the SSIDs to be carried on the AP.
Figure 156: Conceptual view of FortiGate WiFi controller configuration