Configuration overview
A VPN provides secure access to a private network behind the FortiGate unit. You can also enable VPN clients to access the Internet securely. The FortiGate unit inspects and processes all traffic between the VPN clients and hosts on the Internet according to the Internet browsing policy. This is accomplished even though the same FortiGate interface is used for both encrypted VPN client traffic and unencrypted Internet traffic.
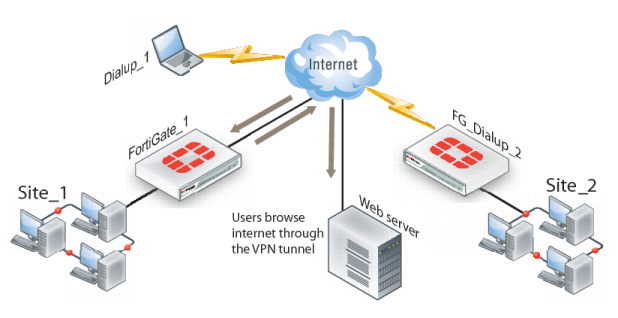
In
Figure 269, FortiGate_1 enables secure Internet browsing for FortiClient Endpoint Security users such as Dialup_1 and users on the Site_2 network behind FortiGate_2, which could be a VPN peer or a dialup client.
You can adapt any of the following configurations to provide secure Internet browsing:
The procedures in this section assume that one of these configurations is in place, and that it is operating properly.
To create an internet-browsing configuration based on an existing gateway-to-gateway configuration, you must edit the gateway-to-gateway configuration as follows: