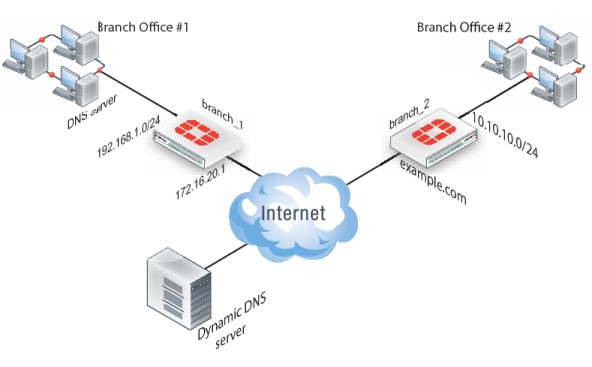
In this scenario, two branch offices each have a FortiGate unit and are connected in a gateway-to-gateway VPN configuration. One FortiGate unit has a domain name (example.com) with a dynamic IP address. See
branch_2 in
Figure 261.
When a remote peer (such as the
branch_1 FortiGate unit in
Figure 261) initiates a connection to
example.com, the local DNS server looks up and returns the IP address that matches the domain name
example.com. The remote peer uses the retrieved IP address to establish a VPN connection with the
branch_2 FortiGate unit.