Packet flow through the GPRS network
To better understand the GPRS network, we will follow the path data takes for a normal connection. For this example a call placed from a mobile phone involves accessing services on the Internet.
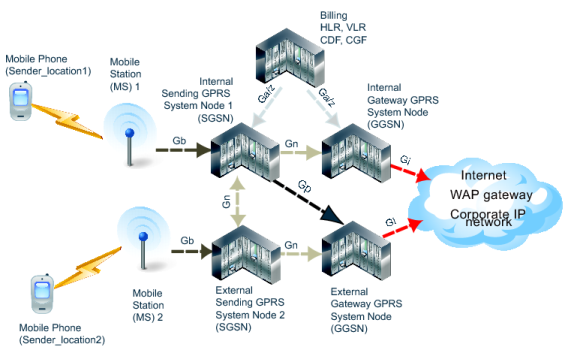
Figure 146: Sample GPRS network topology
1 A mobile phone places a call using a mobile station (MS). This connection between the mobile phone and the MS is a radio connection using one of the radio access technologies. See “Radio Access Technology (RAT) type”.
2. The MS connects to a GPRS System Node (GSN) specifically a Sending GSN. This connection uses the Gb interface and typically uses IP address or Frame Relay.
3. The SGSN checks the mobile phone information located in the home location register (HLR) or visitor location register (VLR) to ensure there is subscriber information for that phone. If this mobile phone is from another network, the SGSN uses the VLR and updates its home carrier’s information with its current location and information. This connection involves the Ga or Gz interfaces, and uses the GTP’ protocol for communication.
4. The SGSN checks to make sure the phone did not transfer this connection from a different MS. If it did, the connection has already been established (along with the billing) and is handed off to this SGSN. If the call is being handed over from another SGSN, it will use the Gn interface between the two SGSNs.
5. The SGSN sends GTP messages to the local external Gateway GSN (GGSN) to create a GTP tunnel for this PDP context to access the Internet. It is possible that a remote GGSN has access to a service, such as a WAP gateway, that the local GGSN is missing. In this situation, the local SGSN uses the Gp interface to connect to the remote GGSN. Both the Gn and Gp interfaces use GTP.
6. The both the local and remote GGSNs connect to external services outside the GPRS network. These services can include a WAP gateway, a corporate IP network directly connected to the GPRS network, or the Internet. The connection from the GGSN to the external services uses the Gi interface.