Figure 130: Create VPN window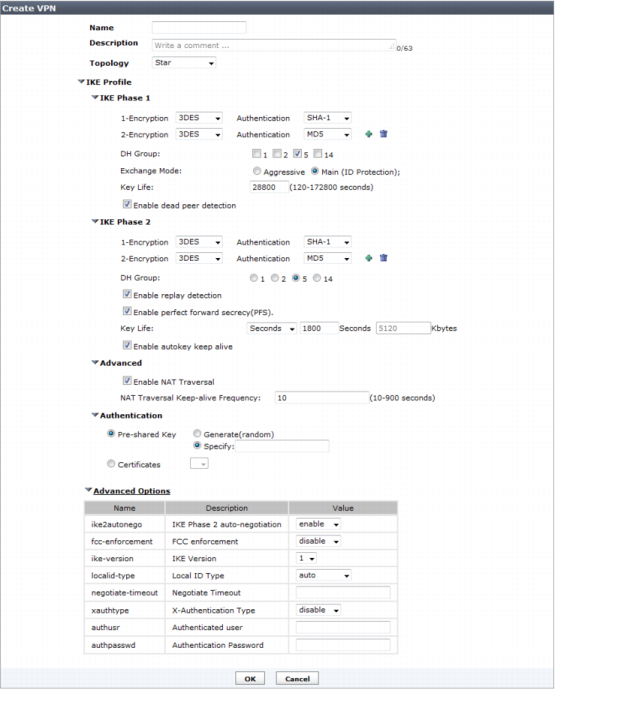


Name | Enter a name for the new VPN configuration. | |
Description | Enter a tunnel description. (Optional) | |
Topology | Choose from Full Mesh, Star, or Dial up. | |
IKE Profile | Create Phase 1 and Phase 2 configurations. | |
IKE Phase 1 | Select the encryption and authentication algorithms used to generate keys for protecting negotiations and add encryption and authentication algorithms as required. You need to select a minimum of one and a maximum of three combinations. The remote peer or client must be configured to use at least one of the proposals that you define. | |
1-Encryption 2-Encryption Authentication | Select one of the following symmetric-key encryption algorithms: • DES — Digital Encryption Standard, a 64-bit block algorithm that uses a 56-bit key. • 3DES — Triple-DES, in which plain text is encrypted three times by three keys. • AES128 — a 128-bit block Cipher Block Chaining (CBC) algorithm that uses a 128-bit key. • AES192 — a 128-bit block Cipher Block Chaining (CBC) algorithm that uses a 192-bit key. • AES256 — a 128-bit block Cipher Block Chaining (CBC) algorithm that uses a 256-bit key. Select either of the following authentication message digests to check the authenticity of messages during phase 1 negotiations: • MD5 — Message Digest 5, the hash algorithm developed by RSA Data Security. • SHA1 — Secure Hash Algorithm 1, which produces a 160-bit message digest. • SHA256 — Secure Hash Algorithm 2, which produces a 256- bit message digest. To specify a third combination, use the Add button beside the fields for the second combination. | |
DH Group | Select one or more Diffie-Hellman groups from DH group 1, 2, 5, and 14. At least one of the DH Group settings on the remote peer or client must match one the selections on the FortiGate unit. Failure to match one or more DH groups will result in failed negotiations. | |
Exchange Mode | Select Main (ID Protection) or Aggressive: • Main mode — the phase 1 parameters are exchanged in multiple rounds with encrypted authentication information. • Aggressive mode — the phase 1 parameters are exchanged in single message with authentication information that is not encrypted. When the remote VPN peer has a dynamic IP address and is authenticated by a pre-shared key, you must select Aggressive mode if there is more than one dialup phase1 configuration for the interface IP address. When the remote VPN peer has a dynamic IP address and is authenticated by a certificate, you must select Aggressive mode if there is more than one phase 1 configuration for the interface IP address and these phase 1 configurations use different proposals. | |
Key Life | Enter the time (in seconds) that must pass before the IKE encryption key expires. When the key expires, a new key is generated without interrupting service. The keylife can be from 120 to 172 800 seconds. | |
Enable dead peer detection | Select this check box to reestablish VPN tunnels on idle connections and clean up dead IKE peers if required. You can use this option to receive notification whenever a tunnel goes up or down, or to keep the tunnel connection open when no traffic is being generated inside the tunnel. | |
IKE Phase 2 | ||
1-Encryption 2-Encryption Authentication | Select one of the following symmetric-key encryption algorithms: • DES — Digital Encryption Standard, a 64-bit block algorithm that uses a 56-bit key. • 3DES — Triple-DES, in which plain text is encrypted three times by three keys. • AES128 — a 128-bit block Cipher Block Chaining (CBC) algorithm that uses a 128-bit key. • AES192 — a 128-bit block Cipher Block Chaining (CBC) algorithm that uses a 192-bit key. • AES256 — a 128-bit block Cipher Block Chaining (CBC) algorithm that uses a 256-bit key. Select either of the following authentication message digests to check the authenticity of messages during phase 1 negotiations: • MD5 — Message Digest 5, the hash algorithm developed by RSA Data Security. • SHA1 — Secure Hash Algorithm 1, which produces a 160-bit message digest. • SHA256 — Secure Hash Algorithm 2, which produces a 256- bit message digest. To specify a third combination, use the Add button beside the fields for the second combination. | |
DH Group | Select one or more Diffie-Hellman groups from DH group 1, 2, 5, and 14. At least one of the DH Group settings on the remote peer or client must match one the selections on the FortiGate unit. Failure to match one or more DH groups will result in failed negotiations. | |
Enable replay detection | Replay attacks occur when an unauthorized party intercepts a series of IPsec packets and replays them back into the tunnel. | |
Enable perfect forward secrecy (PFS) | Perfect forward secrecy (PFS) improves security by forcing a new Diffie-Hellman exchange whenever keylife expires. | |
Key Life | Enter the time (in seconds) that must pass before the IKE encryption key expires. When the key expires, a new key is generated without interrupting service. The keylife can be from 120 to 172 800 seconds. | |
Enable autokey keep alive | Select the check box if you want the tunnel to remain active when no data is being processed. | |
Enable auto-negotiation | When enabled, auto-negotiate initiates the phase 2 SA negotiation automatically, repeating every five seconds until the SA is established. | |
Advanced | ||
Enable NAT Traversal | Select the check box if a NAT device exists between the local FortiGate unit and the VPN peer or client. The local FortiGate unit and the VPN peer or client must have the same NAT traversal setting (both selected or both cleared) to connect reliably. | |
NAT Traversal Keep-alive Frequency | If you enabled NAT-traversal, enter a keepalive frequency setting. | |
Authentication | ||
Pre-shared Key | If you selected Pre-shared Key, enter the pre-shared key that the FortiGate unit will use to authenticate itself to the remote peer or dialup client during phase 1 negotiations. You must define the same key at the remote peer or client. | |
Certificates | If you selected RSA Signature, select the name of the server certificate that the FortiGate unit will use to authenticate itself to the remote peer or dialup client during phase 1 negotiations. | |
Advanced Options | ||
FCC Enforcement | Select to enable or disable FCC Enforcement. | |
IKE Version | Select the version of IKE to use. This is available only if IPsec Interface Mode is enabled. For more information about IKE v2, refer to RFC 4306. | |
Local ID Type | Select auto, fqdn, user-fqdn, keyid, address, or asn1dn from the drop-down menu. | |
Negotiate Timeout | Enter a numerical value for the negotiate timeout period. | |