SNMP traps & queries
System > Config > SNMP enables you to configure the FortiADC appliance’s simple network management protocol (SNMP) agent to allow queries for system information and to send traps (alarms or event messages) to the computer that you designate as its SNMP manager. In this way you can use an SNMP manager to monitor the FortiADC appliance.
Before you can use SNMP, you must activate the FortiADC appliance’s SNMP agent and add it as a member of at least one community. You must also enable SNMP access on the network interface through which the SNMP manager connects. (See
“Configuring the network interfaces”.)
On the SNMP manager, you must also verify that the SNMP manager is a member of the community to which the FortiADC appliance belongs, and compile the necessary Fortinet-proprietary management information blocks (MIBs) and Fortinet-supported standard MIBs. For information on MIBs, see
“MIB support”.
| Failure to configure the SNMP manager as a host in a community to which the FortiADC appliance belongs, or to supply it with required MIBs, will make the SNMP monitor unable to query or receive traps from the FortiADC appliance. |
To configure the SNMP agent
1. Add the MIBs to your SNMP manager so that you will be able to receive traps and perform queries. For instructions, see the documentation for your SNMP manager.
2. Go to System > Config > SNMP.
To access this part of the web UI, your administrator's account access profile must have
Read-Write permission to items in the
System category. For details, see
“Permissions”.
3. Configure the following:
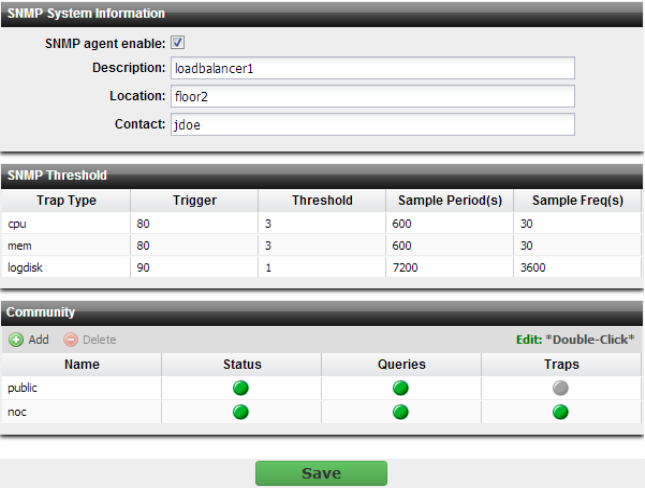
Setting name | Description |
SNMP agent enable | Enable to activate the SNMP agent, so that the FortiADC appliance can send traps and receive queries for the communities in which you enabled queries and traps. For more information on communities, see “Configuring an SNMP community”. |
Description | Type a description or comment about the FortiADC appliance, such as dont‑reboot. The description can be up to 35 characters long, and can contain only letters (a-z, A-Z), numbers, hyphens ( ‑ ) and underscores ( _ ). |
Location | Type the physical location of the FortiADC appliance, such as floor2. The location can be up to 35 characters long, and can contain only letters (a-z, A-Z), numbers, hyphens ( ‑ ) and underscores ( _ ). |
Contact | Type the contact information for the administrator or other person responsible for this FortiADC appliance, such as a phone number (555-5555) or name (jdoe). The contact information can be up to 35 characters long, and can contain only letters (a-z, A-Z), numbers, hyphens ( ‑ ) and underscores ( _ ). |
4. Click Save.
See also


